| Duration: | 01/2025 - 12/2028 |
| Contracting Authority/ Sponsors: | Federal Ministry of Economic Affairs and Energy (BMWE) |
| Project Partners: | greenventory GmbH, Stadtwerke Konstanz GmbH, Fraunhofer ISE, VIVAVIS AG, Next2Sun GmbH, Swistec GmbH |
| Project Focus: |
DiGO 2.0 – Distribution Grid Optimization 2.0

The energy, transport and heating transition represents a considerable challenge for the electricity grids. According to current planning guidelines, the increased use of heat pumps and electric vehicles would require a massive expansion of the distribution grids. This would result in high costs and could slow down the transition to a CO2-neutral society.
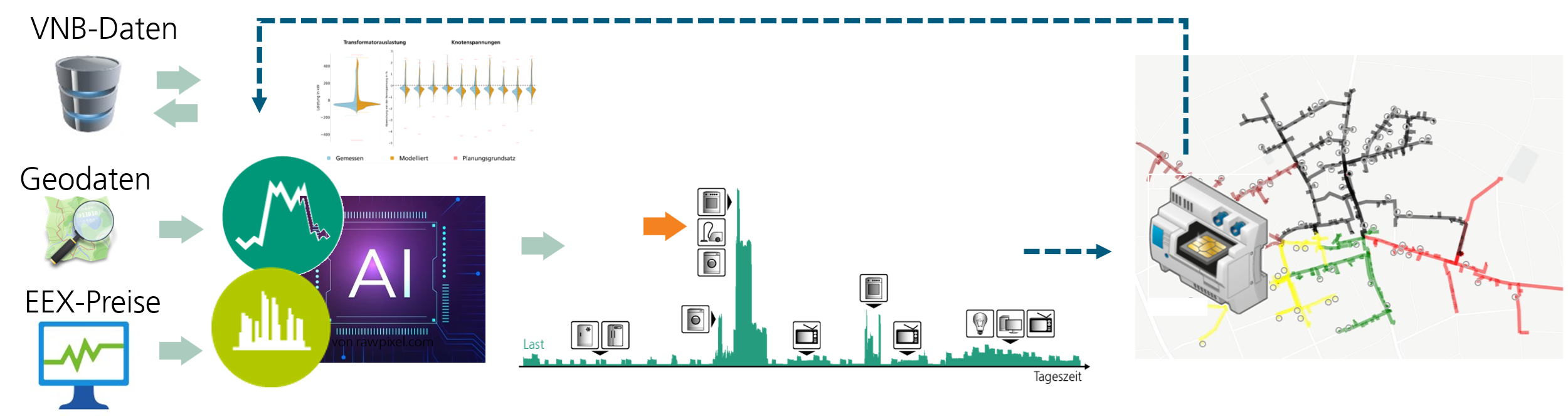
Grid operation platforms can use smart metering systems (iMSys) and control boxes to record grid conditions and reduce grid loads through targeted control interventions, incentivized by variable grid charges. If the grid load can be reduced through targeted incentives, this must be taken into account in grid planning in order to minimize grid expansion.
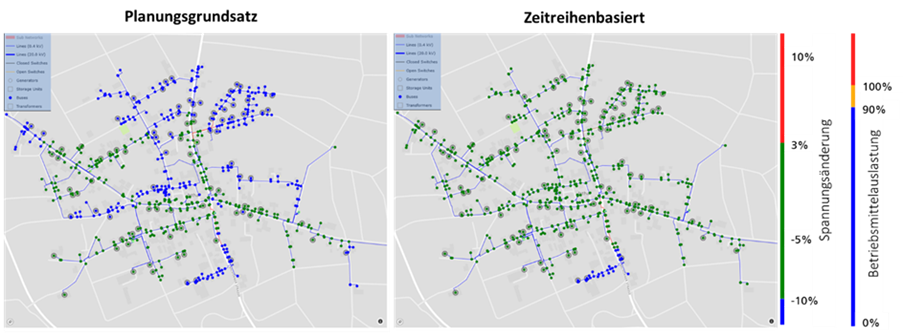
According to studies, grid expansion costs of up to 50 billion euros can be saved in the low-voltage grid alone through grid-friendly operation management. The aim of the project is therefore to implement grid operation management with smart metering systems in practice and to develop planning principles that integrate this grid operation management. To achieve this, the classic grid planning principles based on unrealistically high loads must be replaced. Instead, principles should be used that are based on time series and take into account incentive instruments for grid relief. To this end, adaptive methods for load, generation and flexibility forecasts will be developed and validated with a field test. These forecasts will be used to test and further develop approaches for incentivizing grid-friendly behaviour in accordance with §14a and c EnWG. The data from the real laboratory will be used to quantitatively incorporate such flexibilities into grid planning. The interaction of the components, consisting of algorithms, grid operation platform, iMSys, control boxes and customer systems, is tested both in the laboratory and in the field.
A grid capacity map (GCM) that determines connection costs and available grid capacities is being developed to enable plant project planners to participate in flexibility-based planning. If a requested system causes temporary overloads, times with potential restrictions are to be reported back so that these can be included in profitability calculations. Target grid planning tools are being further developed in order to take into account connection requests that have been earmarked in the GCM and to determine the effects of the control system on the German grid expansion requirements.