In the field of data analysis using artificial intelligence methods, we use both small and big data approaches to discover new correlations and property relationships in the data generated by our laboratory infrastructure. In addition, we analyze market and industry data with our partners and improve operations strategies and quality assurance procedures. Our in-depth domain knowledge, which spans all relevant areas of battery research – from material development and electrochemical processes to production and operating strategies – is incorporated into the interpretation of this data.
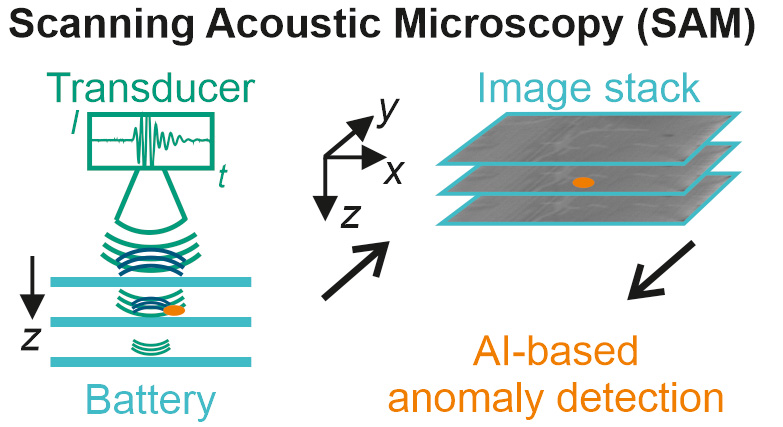
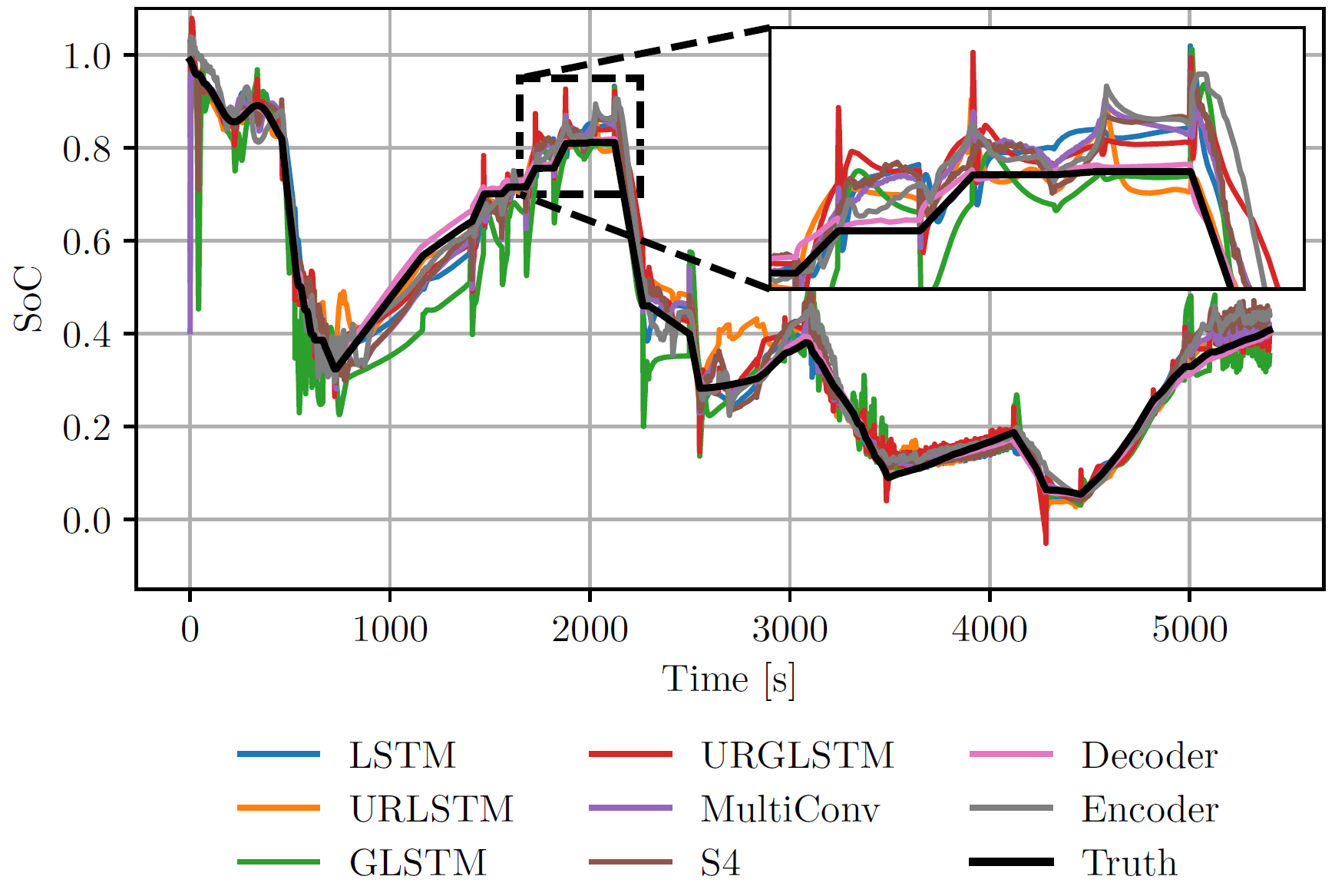
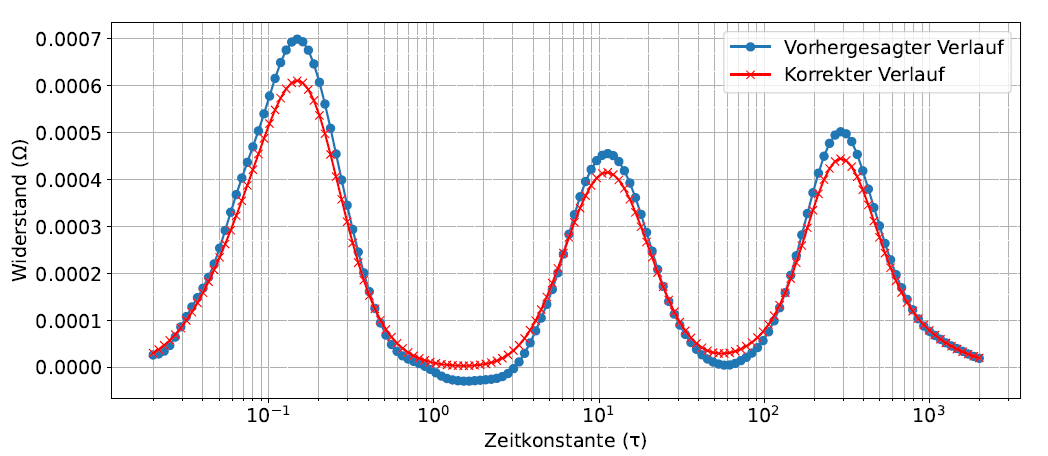
We use advanced signal and data processing methods to detect new effects and correlations using artificial intelligence. We use computer vision models to segment and classify objects and anomalies and analyze time series data using principle component analysis, independent component analysis and other signal processing methods.