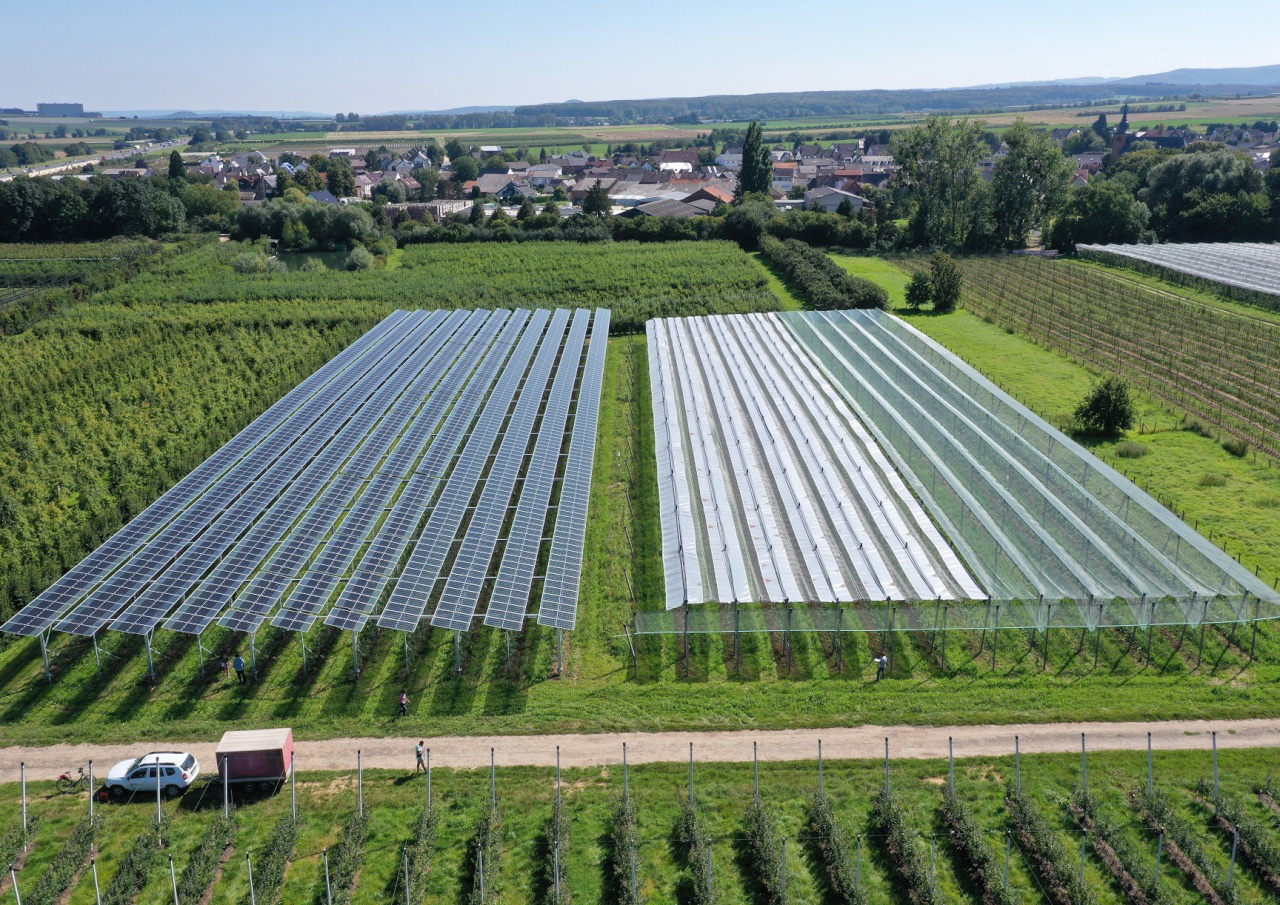
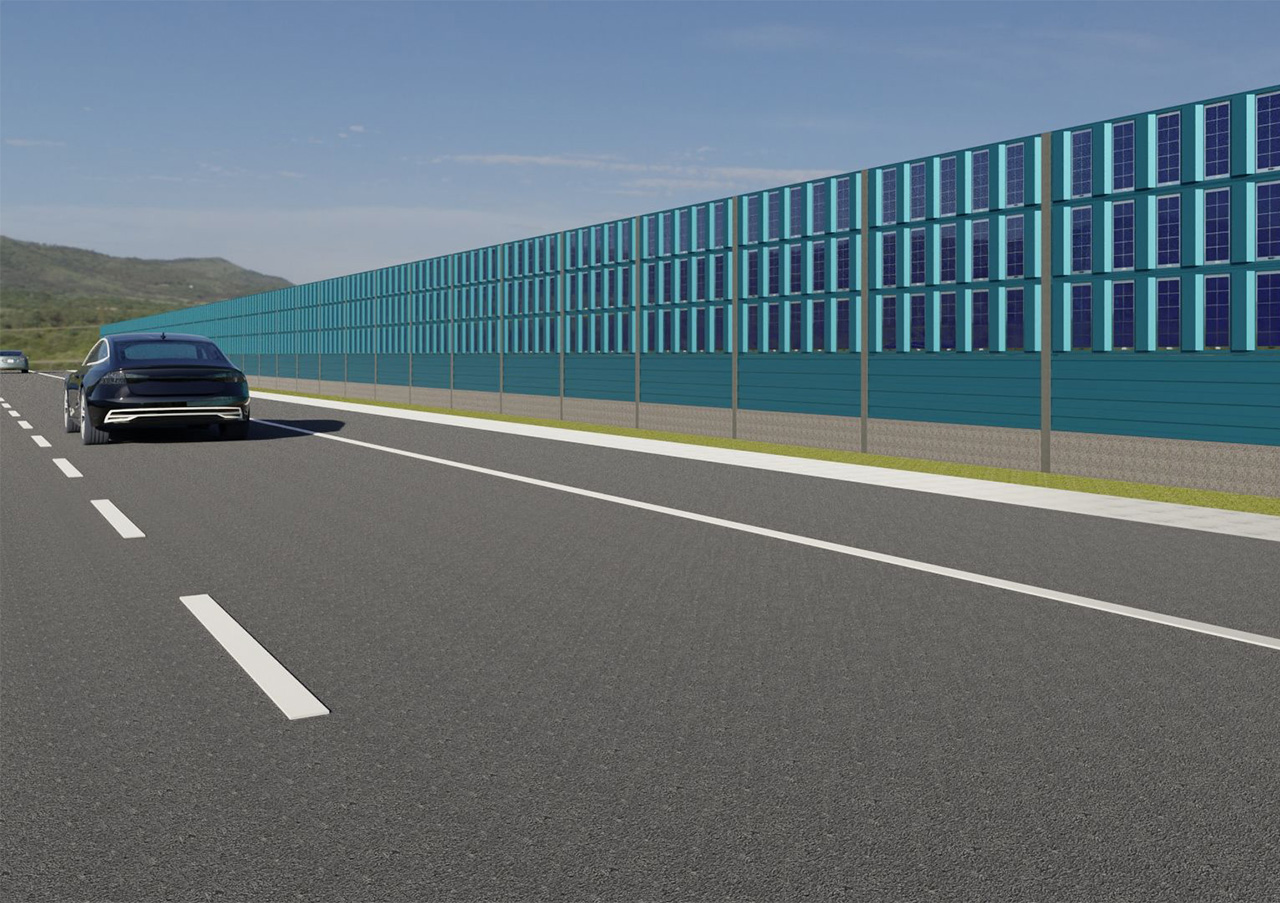
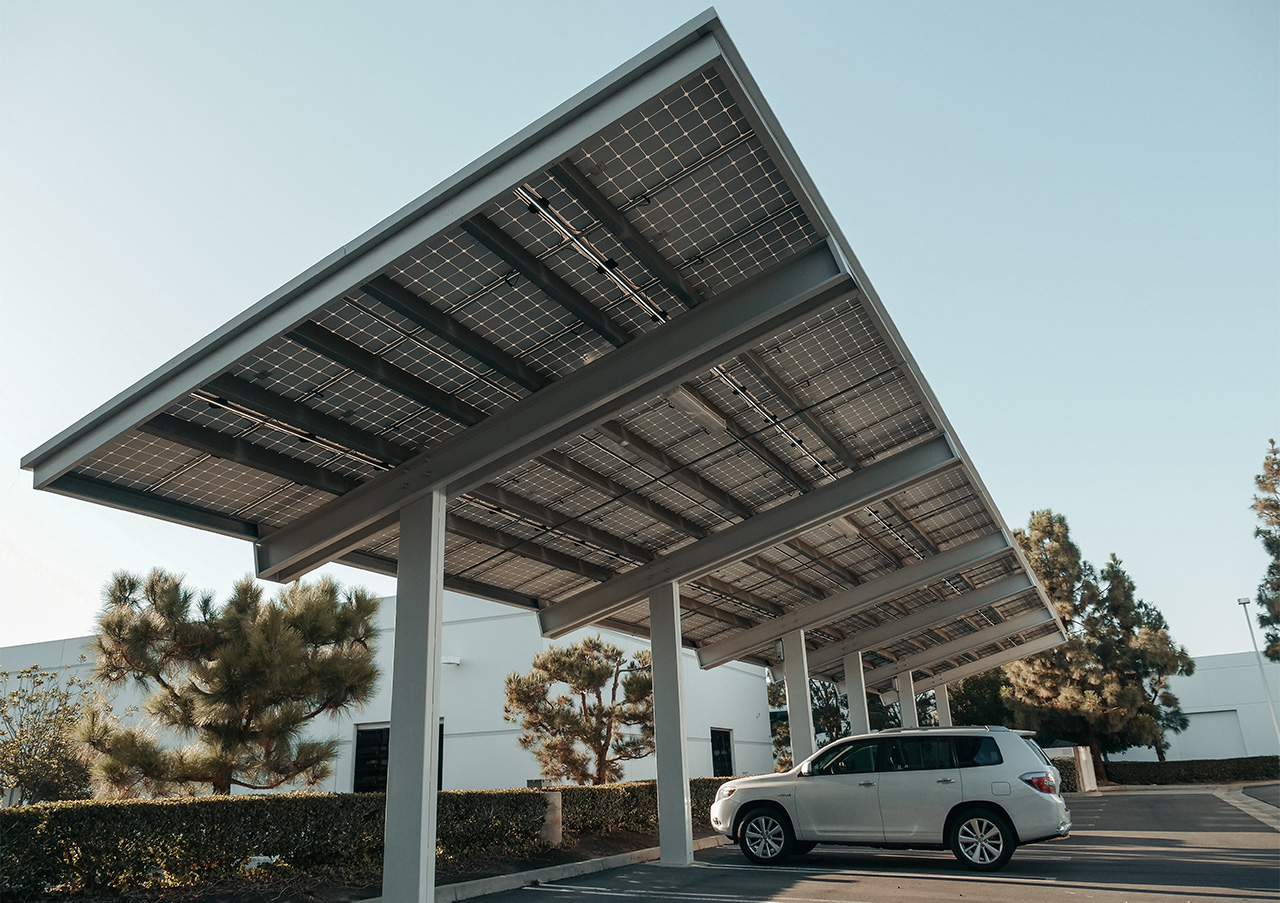
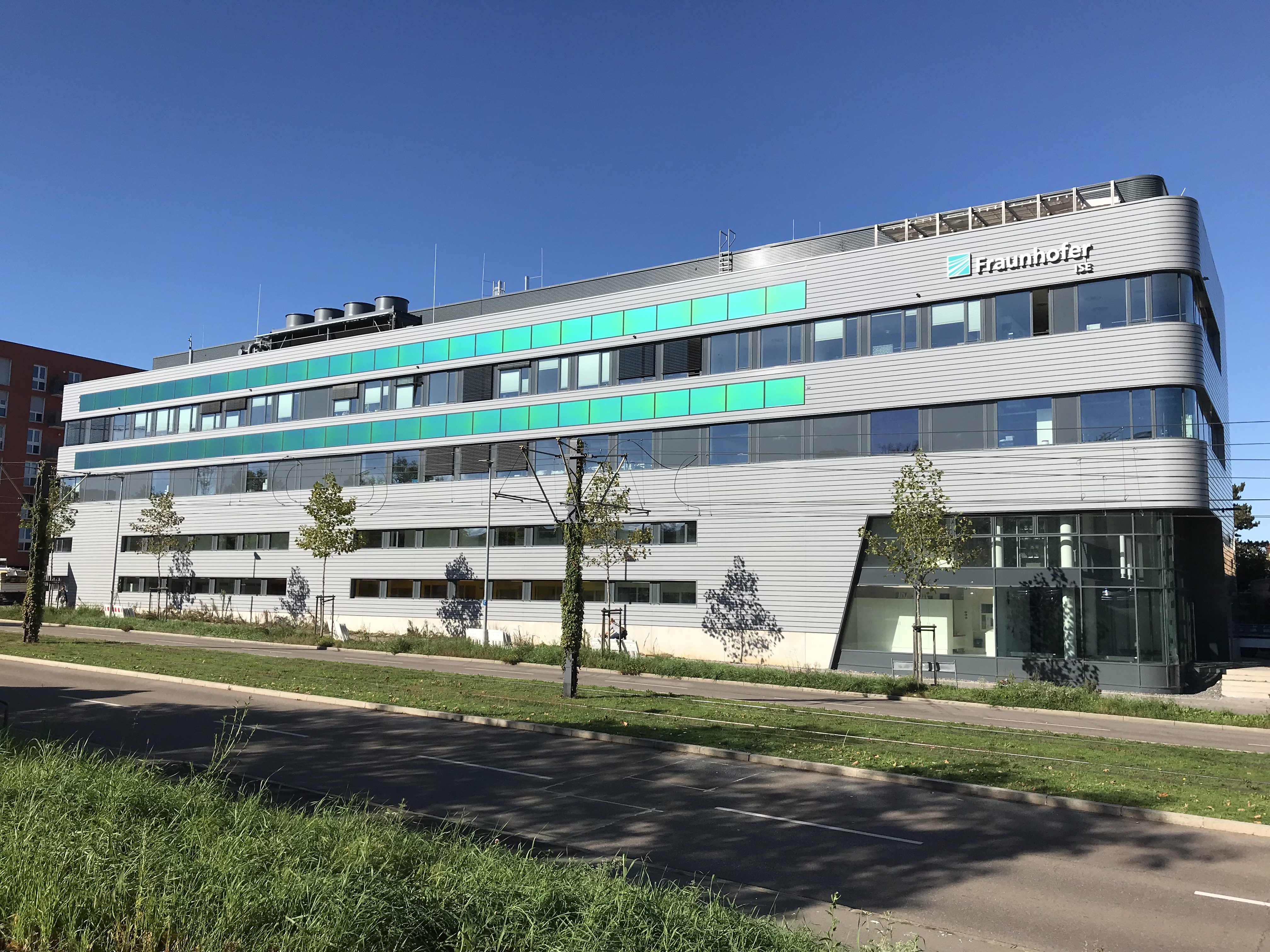
Urban photovoltaics (Urban PV) uses sealed surfaces in cities and municipalities to generate renewable electricity and make the locations visually appealing. Examples include large parking lots, public squares or sports facilities where photovoltaics are installed to provide shade, in combination with light, with charging infrastructure for electromobility or rain protection. This enhances the places for the user and makes the energy transition a positive experience. PV systems can serve as advertising signs on roads, integrate WiFi, 5G mobile communications or monitoring functions. Further advantages of this technology are the often short connection to the grid and the additional sun and weather protection provided by the roofs. The dual use avoids an additional burden on the environment and, if the systems are well designed, creates attractive and exciting squares and streetscapes.
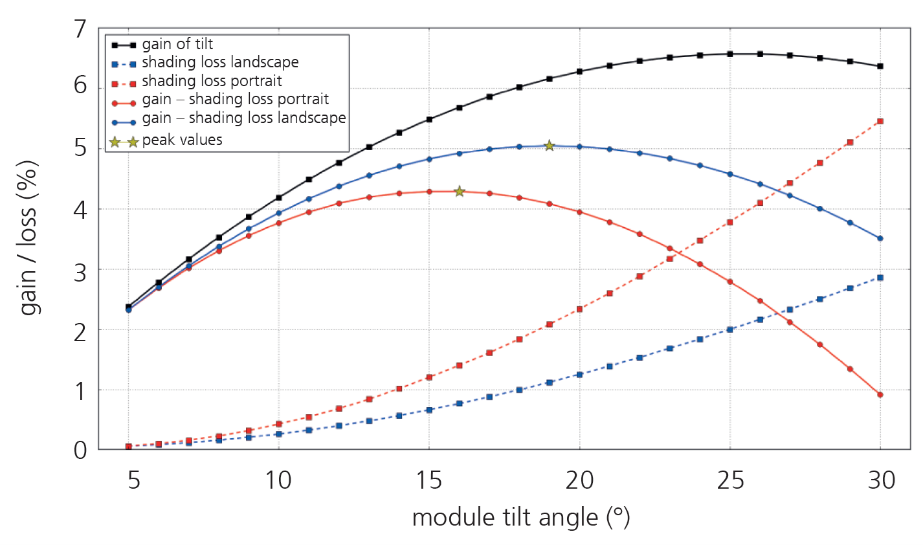
Urban PV installations have to meet high demands in terms of design and functionality and therefore usually require individual solutions. Challenges of this technology can include higher shading effects from surrounding buildings or trees, special regulatory requirements, as well as higher static and building code requirements with regard to stability, mechanical load, noise absorption or the reflection effects of the systems.
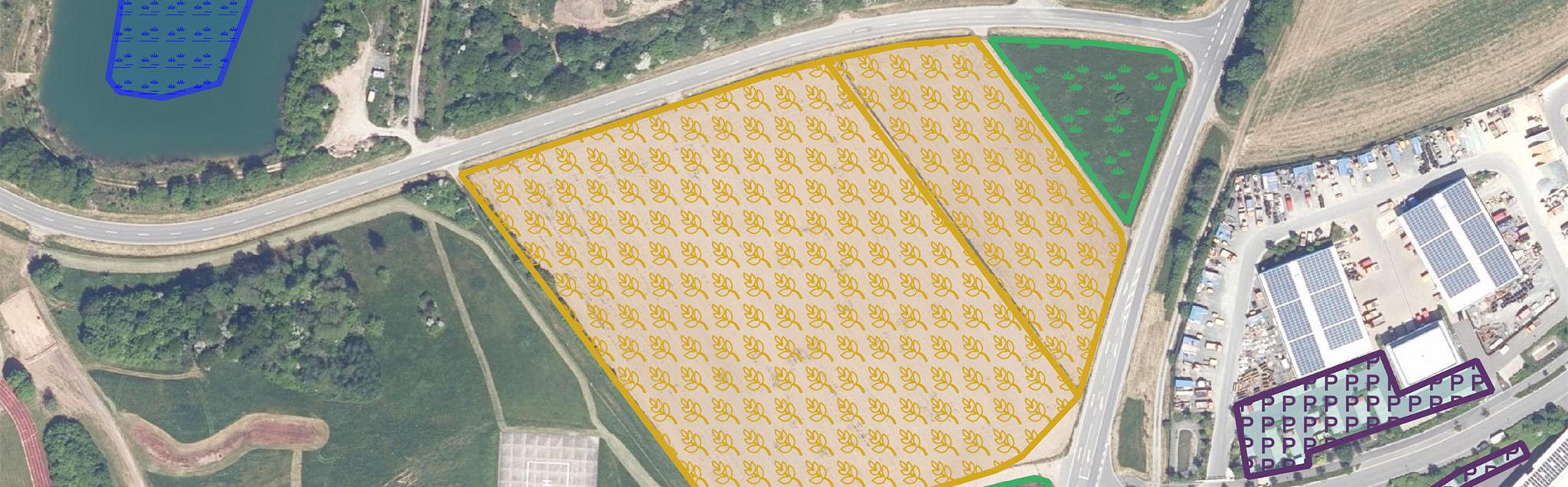
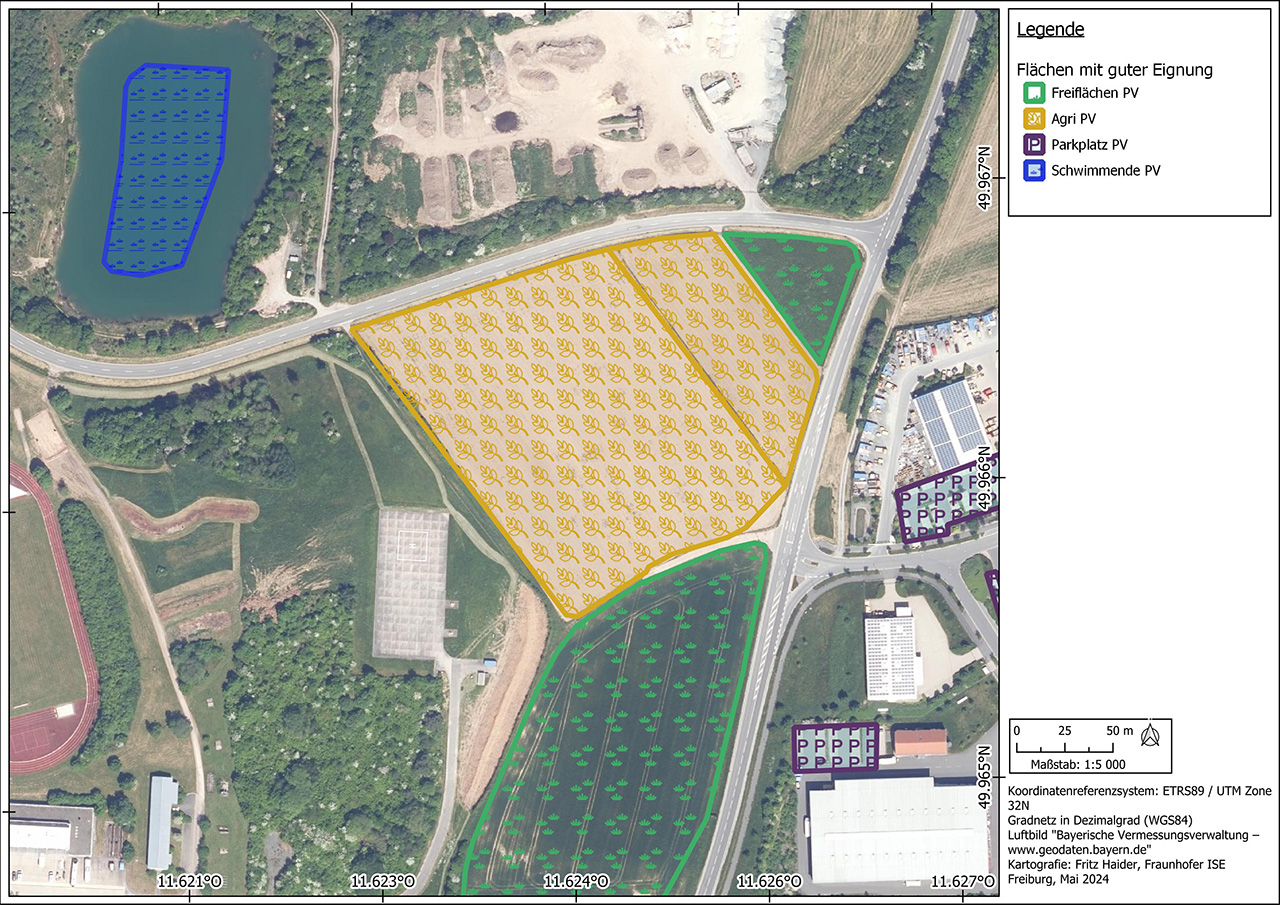
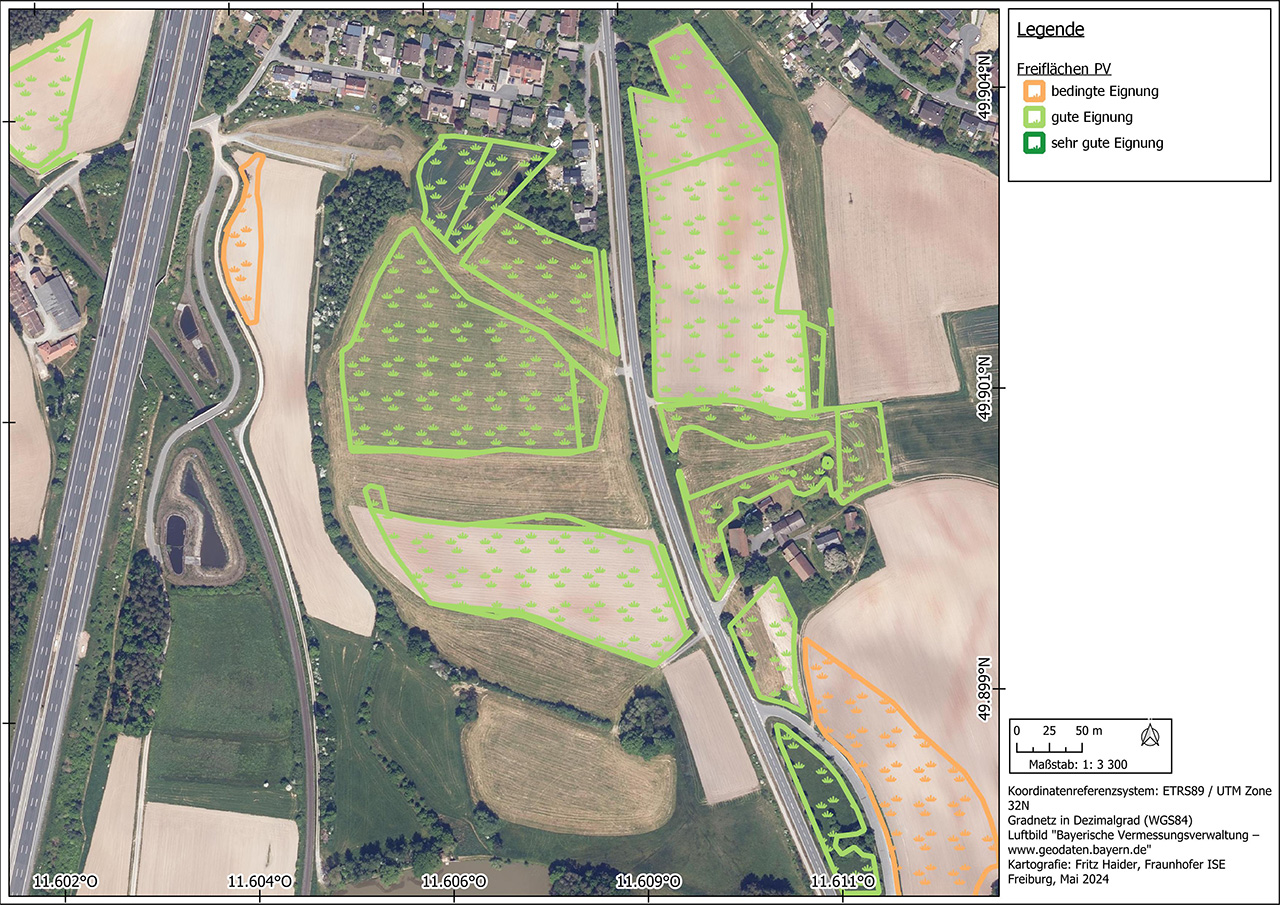
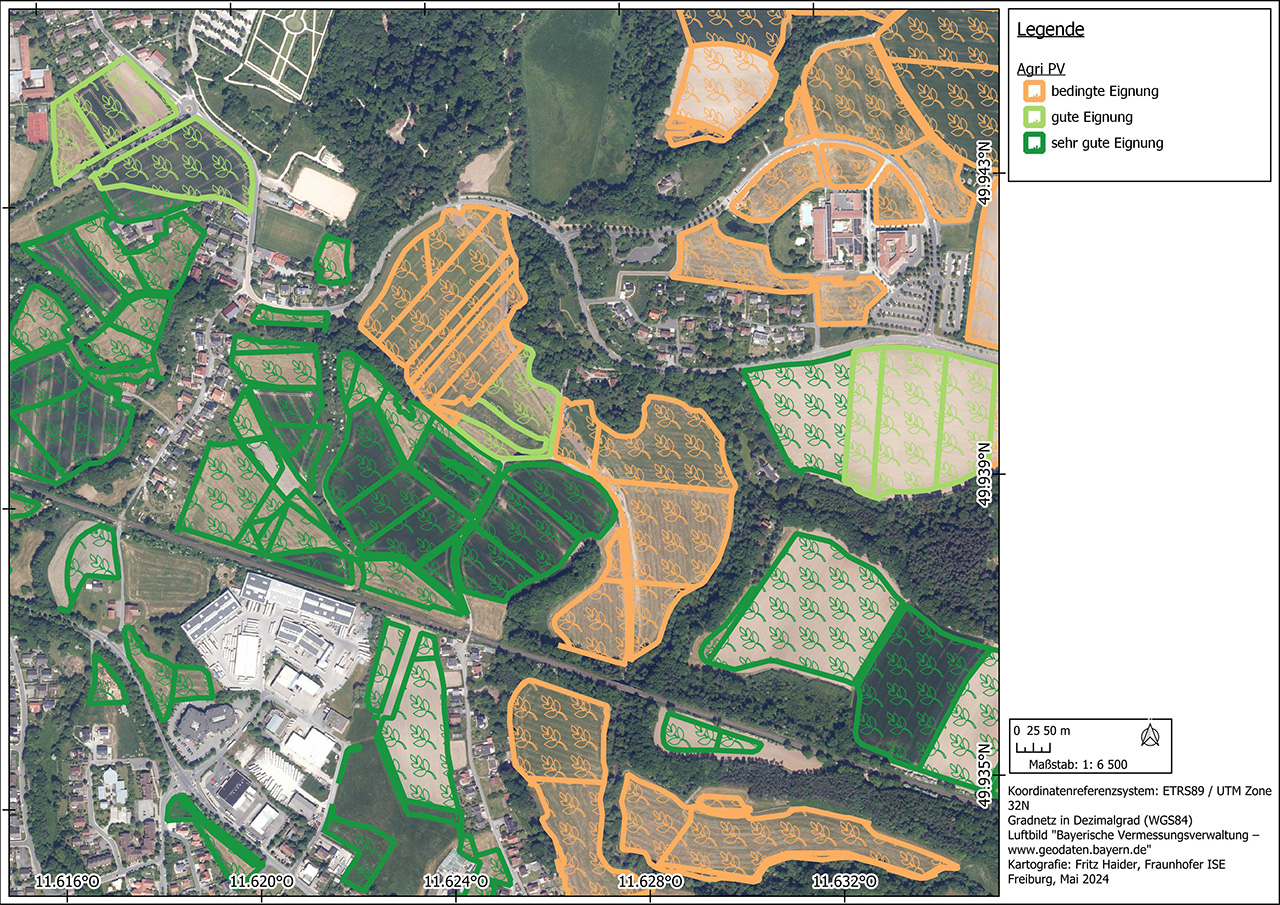
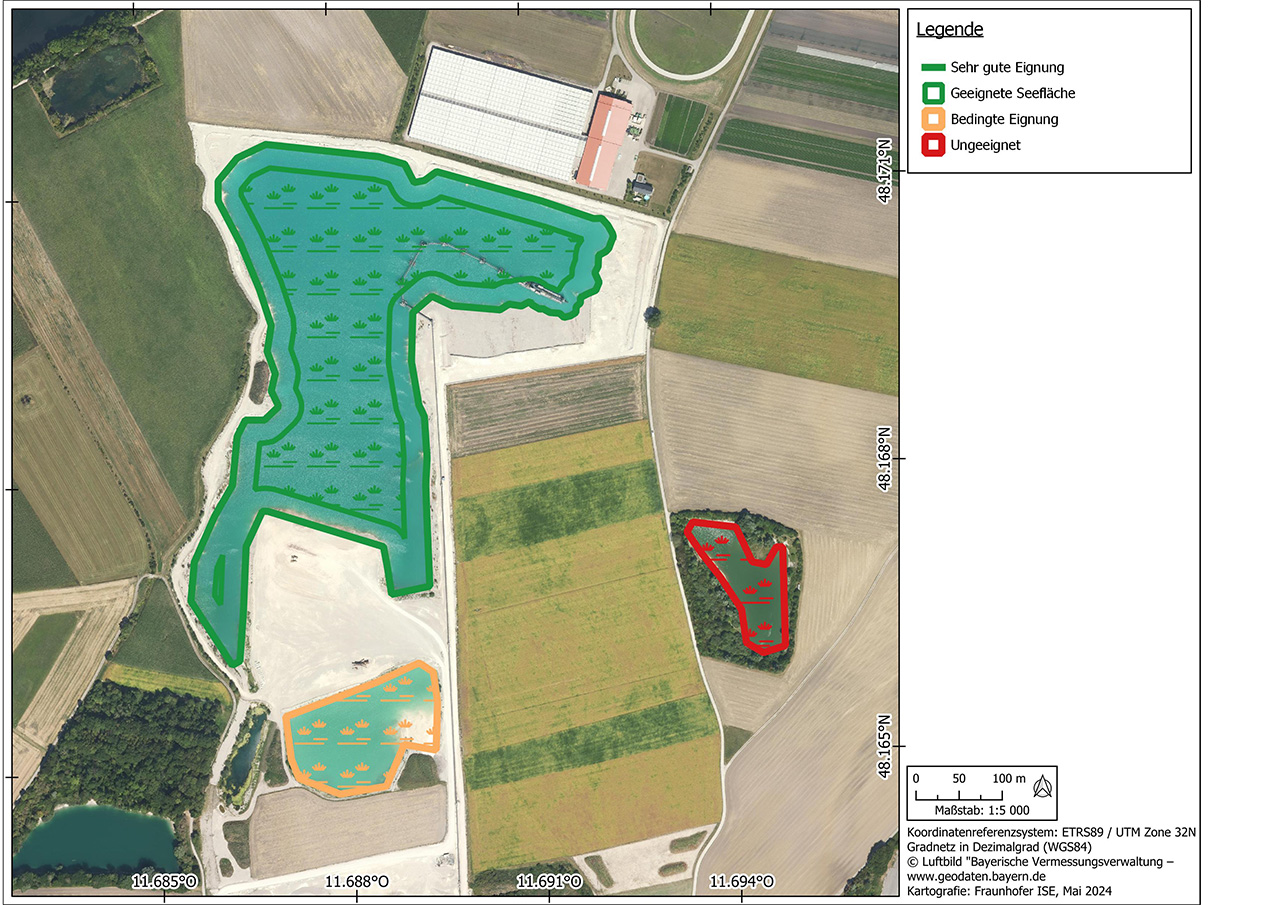
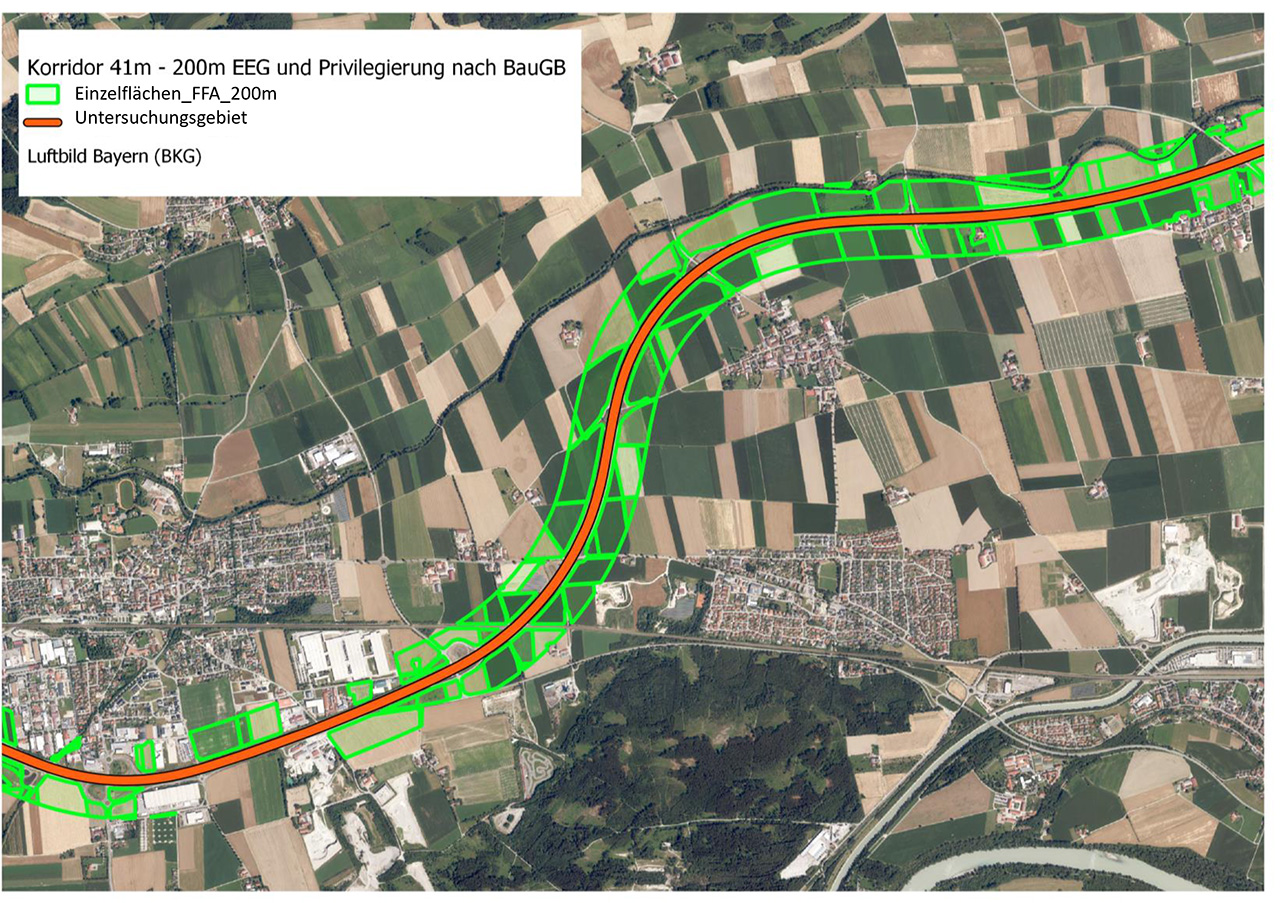
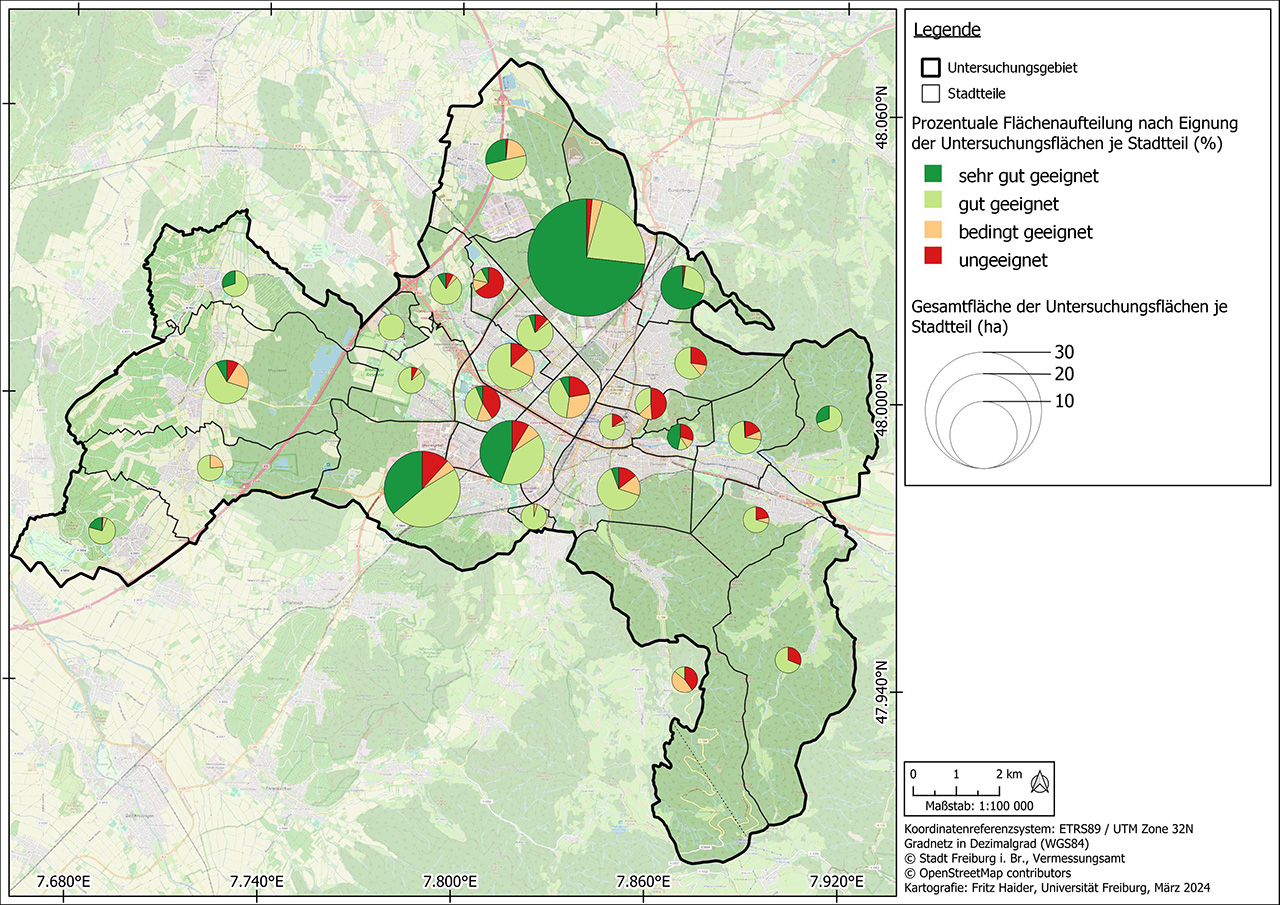
To analyze the PV potential on parking lots, a data set of all relevant study areas is first created based on data collected by the authorities or freely available data such as the OpenStreetMap database. In a site suitability analysis, these areas are then checked for their suitability for the construction of parking lot photovoltaic systems according to criteria previously agreed with the client. These include factors such as shading, inclination, size of the area and distance to the nearest electricity grid feed-in point. Once the unsuitable areas have been excluded, the technical performance and energy potential is calculated, which can be carried out for entire parking lot roofs as well as for individual parking space roofs.
Request potential analysis for UPV systems