News #31
INFAB project develops cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternatives to lithium-ion batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are the state of the art in stationary energy storage, but parts of the raw material extraction are controversial due to environmental and social problems. The Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE has therefore joined forces with partners in the INFAB project to research an alternative technology based on zinc-ion batteries. The project covered all process stages, from the development of cell chemistry and manufacturing processes to the battery management system.
The current challenges of research into stationary battery storage lie in the conflicting areas of safety, durability, investment costs and application-specific storage costs (Levelized Cost of Energy Storage, LCOS for short), the availability of raw materials and environmental and social compatibility throughout the entire product life cycle. "The INFAB research project is focusing on high-performance zinc-ion battery technology. It stands out due to the simplicity of the system structure combined with a high level of safety, non-toxic battery components and the possibility of environmentally and socially compatible raw material extraction within the EU. The technology also offers the potential for low costs per kilowatt hour," explains project manager Harald Gentischer.
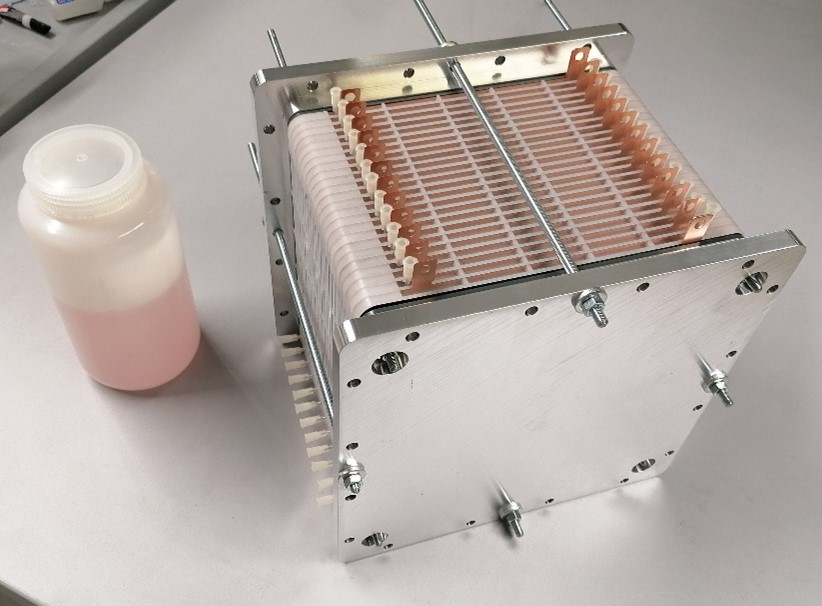
The INFAB project partners developed an innovative cell chemistry with water-based electrolytes, which formed the basis for the architecture of a stationary zinc-ion battery system. The University of Stuttgart was responsible for modeling the zinc-ion battery cell technology. The project team focused on a modular, universal module structure with bipolar interconnection, which allows simple disassembly for later recycling. One innovation is the porous electrode structures developed by Fraunhofer ISE in the project based on a dry coating process that allows high coating thicknesses on a millimeter scale. "In contrast to the current state of the art, which consists of a solvent-based wet coating, the complex and energy-intensive drying process can be dispensed with here," says Harald Gentischer.
The project partner acp systems AG developed the innovative battery cells and modules and the production technology for the zinc-ion battery modules. Helmut Hechinger GmbH was responsible for production planning and the development of the battery management system ystems.
The battery cell and stack prototypes for stationary electricity storage applications at the 48 V voltage level were successfully built and characterized at the end of the project. "We were able to demonstrate a high cost reduction potential compared to competing technologies, especially the lithium-ion battery with LFP cathodes. There are still challenges with regard to the energy density and long-term stability of zinc-ion batteries," says Dr. Oliver Fitz, Group Leader Battery Cell Technology at Fraunhofer ISE.
In follow-up projects, the consortium is planning further research into water-based and organic cell chemistries for zinc-ion batteries and sodium-ion batteries.
Downloads and Links
Last modified: