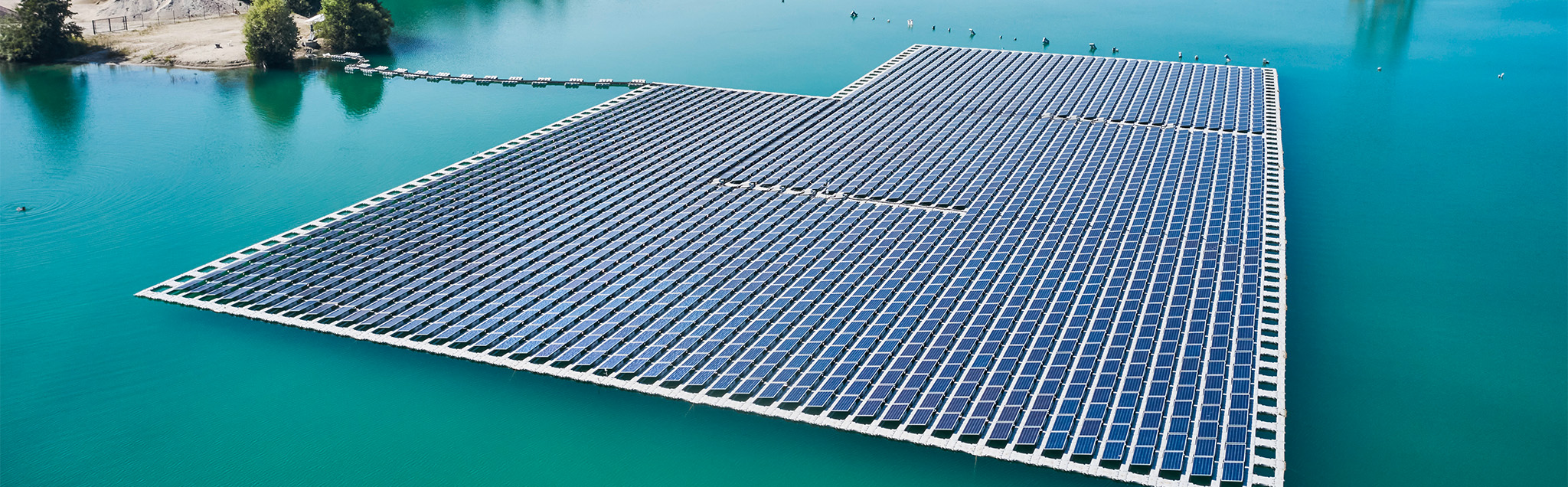
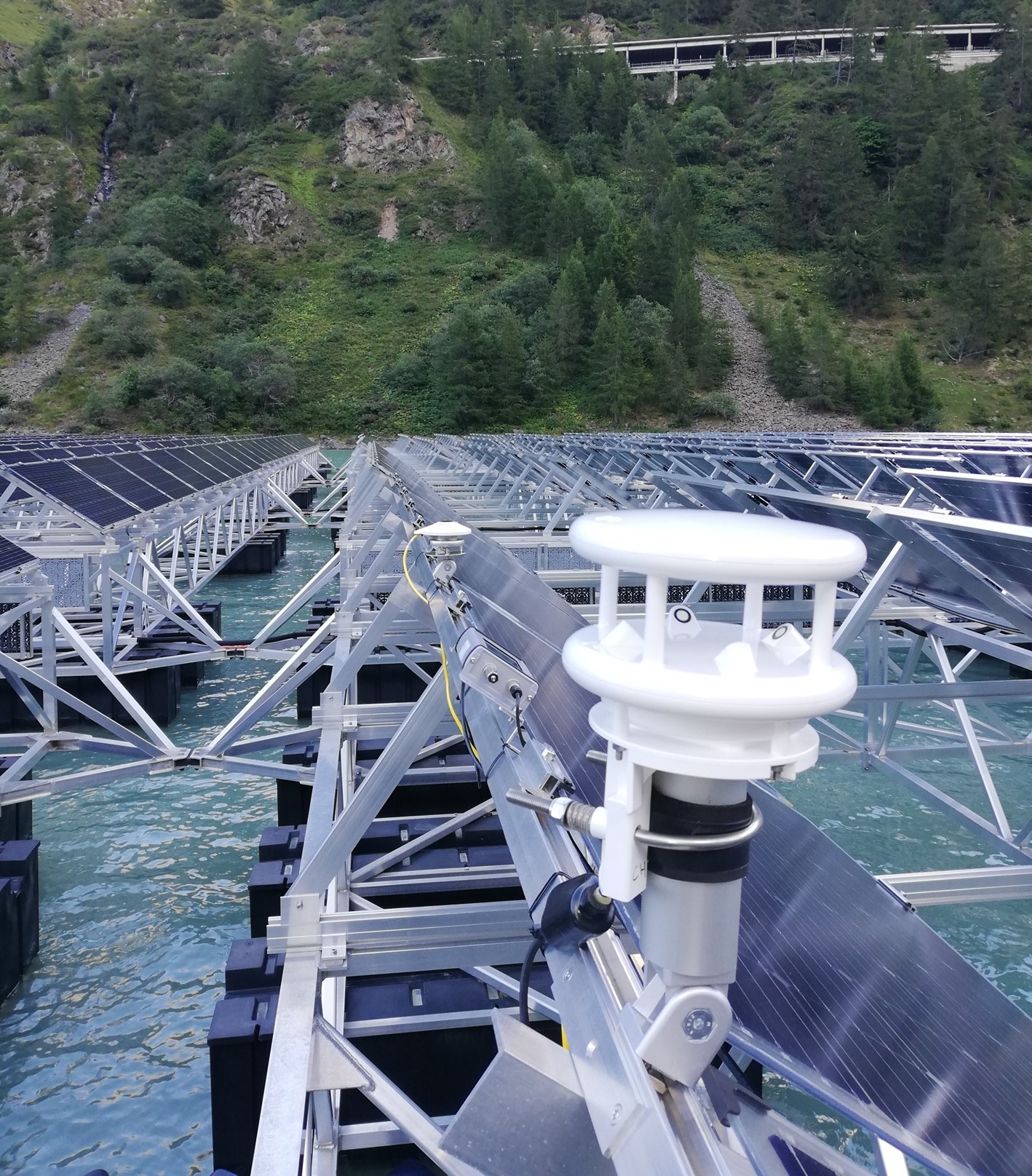
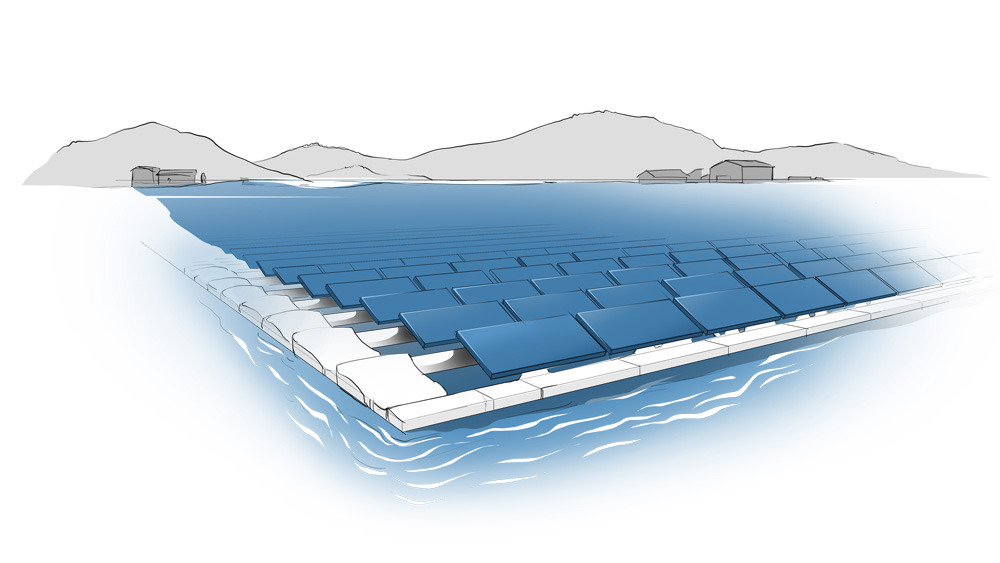
Floating photovoltaics refers to photovoltaic power plants whose modules are mounted on floating bodies of water or on the sea. They generate solar power without occupying valuable land areas.
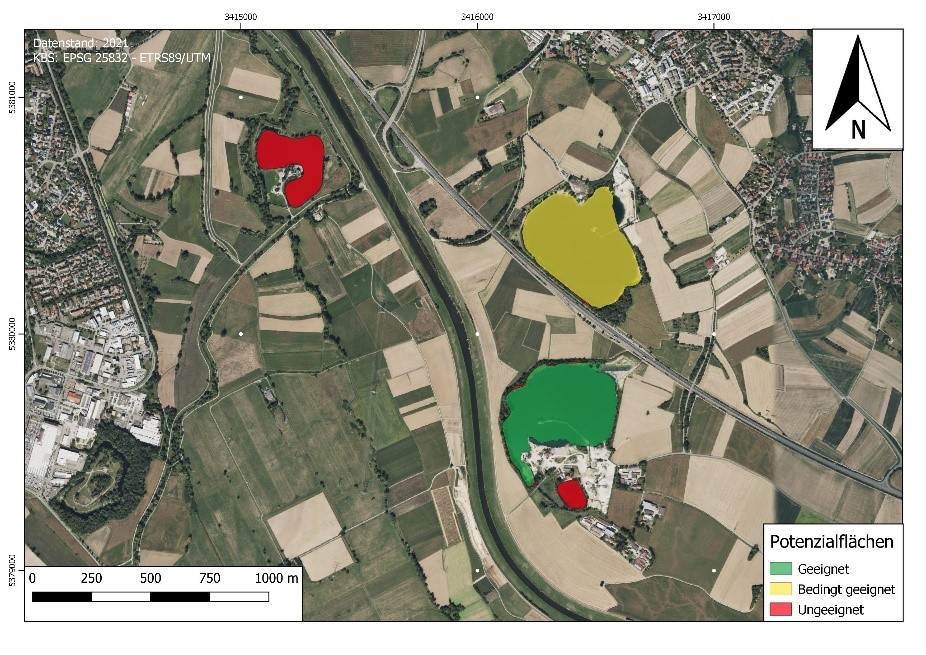
In Germany, flooded open-cast mining areas, gravel pits and, in some cases, reservoirs can be considered. There are sufficient suitable areas on artificial lakes. According to a recent study by Fraunhofer ISE, these have a technical potential of 44 GWp.
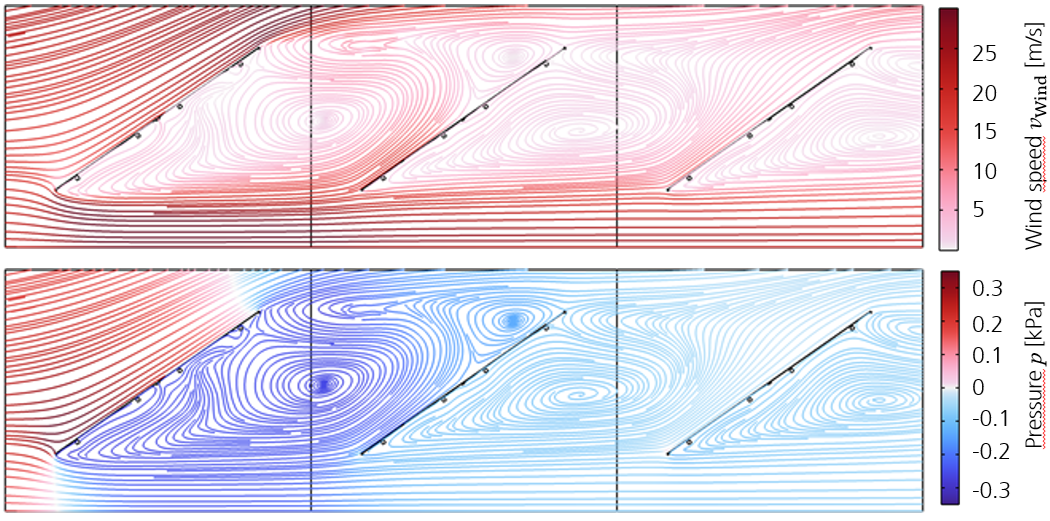
With our many years of experience in module and system technology and in power plant monitoring, we can analyze the specific requirements for floating photovoltaics. Our "Zenit" software is able to create yield forecasts for floating PV systems. This takes into account, for example, system design, module orientation and environmental variables such as air temperature.
We offer studies, analyses, PV and water monitoring for planning offices, EPCs and plant operators.