| Duration: | October 2014 - October 2018 |
| Contracting Authority/ Sponsors: | German Federal Ministry of Economic Affairs and Energy (BMWi) |
| Project Partners: | SMA Solar Technology AG, MWH Märkisches Werk GmbH, Fraunhofer Institute for Wind Energy and Energy System Technology IWES, Institute for Electrical Power Engineering of Technical College Cologne, Energiebau Solartstromsysteme GmbH |
| Project Focus: |
PV Diesel – System Optimization and Operating Strategies for Universally Applicable, Scalable PV Diesel Power Plants of the Multi-Megawatt Class

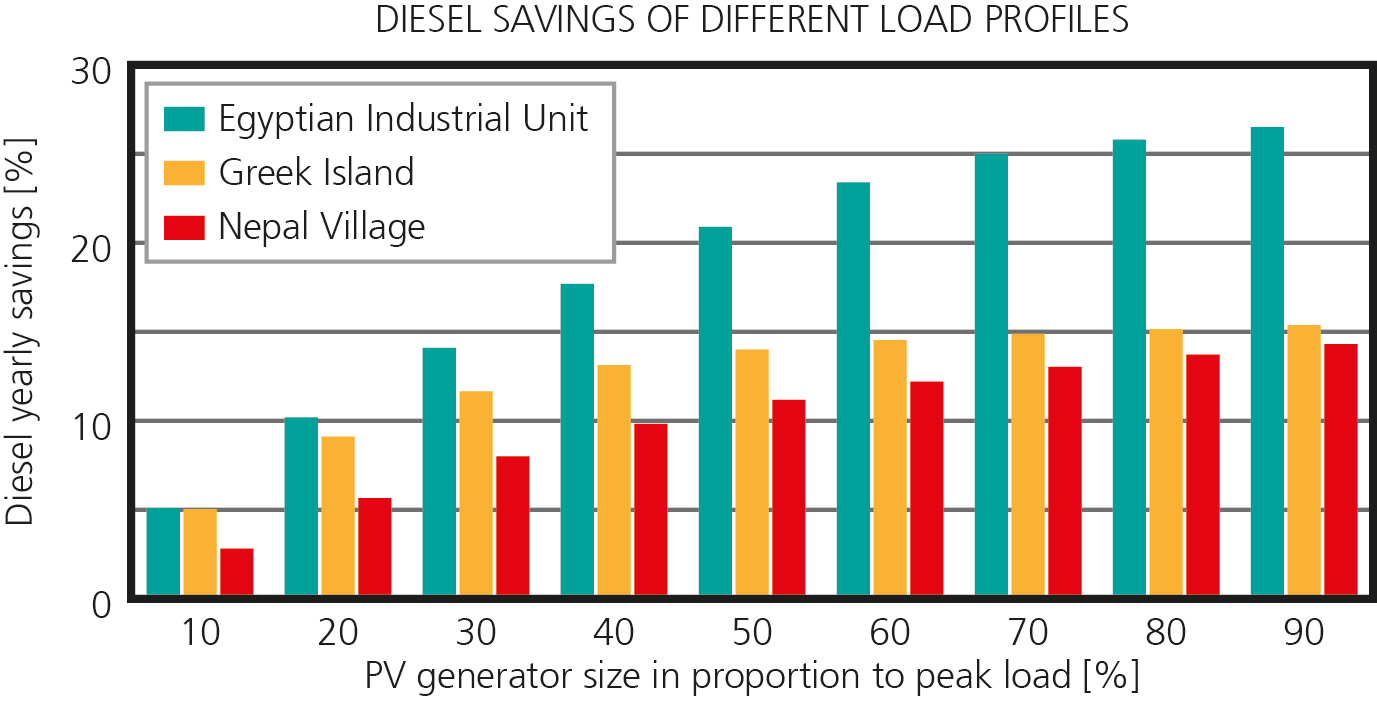
Many villages, cities, islands and industrial operations worldwide in regions without grid connection are supplied with electricity from diesel generators. This established market for diesel generators must be replaced in relevant parts with sustainable energy supply systems, in particular with photovoltaics, and/or expanded in terms of the worldwide electrification programs. Within the scope of the joint “PV Diesel” research project, the interaction of photovoltaics and diesel generators should be researched and still open scientific, technical questions clarified. The key objective is to establish suitable system solutions and to cover the overall system diversity with suitable, standardized components, as well as significant cost reductions and improved reliability.
For this purpose, companies of the PV system technology sector, PV plant engineering and diesel system providers must work together closely. The specific R&D objective is the development of fully functional, practical, optimized system solutions that can be flexibly customized to the respective application case. For this purpose, we first developed simulation models with different detailing depth as tool for component development and for the investigations regarding system concept, grid and system stability, system optimization, and system design methods. Among others, power plants should be dimensioned with respect to different optimization scenarios, e.g., diesel saving potentials, using these system tools based on a detailed load analysis. We used the Matlab® system environment to prepare the models of diesel generators, PV, fuel saver, loads, and load management systems. Based on three case studies (an Egyptian industrial plant, a Greek island, and a Nepalese village), we have calculated diesel savings between 5 % and 30 % in fuel saver mode. Using our load management, additional saving potentials of 6 % to 15 % are possible depending on the existing loads. Higher savings for fuel saver and load management are possible with excellent matching between load and solar profile. Battery models are added to the simulation in the next step. The simulation environment and models are then considered in the design tool for PV diesel power plants.