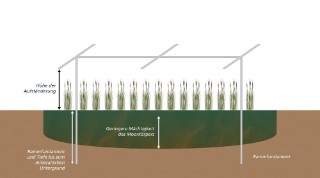
In the HUMAX research project, various measures to build humus and improve soil carbon content will be investigated in different combinations. The aim is to identify possible synergies of the measures and to show combined application options. A unique feature of the HUMAX project is that these measures are to be applied in agrivoltaic systems (AV) and agroforestry systems (AFS). In an innovative approach of the HUMAX project, humus increasing measures (cover crops, winter greening, compost application, etc.) will be combined and tested with other promising measures such as biochar. By combining the various humus-building measures, new ways shall be found to maximize the build-up of humus, the carbon sequestration and therefore the function of the soil as a carbon sink. For this purpose, the effects of the combinations of measures on soil carbon and agriculture in AV and AFS systems are examined. Building on this, a modular system will be developed that will allow farmers to put together the best possible combination of measures for targeted carbon and humus management in their business, given their general conditions at the site. As part of the project, research at the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems focuses on the systemic and microclimatic analysis of various AV systems. The results are statistically evaluated and modeled in connection with the agronomic and soil physical studies in order to optimize AV systems with regard to microclimatic changes and build-up of soil organic carbon i.e., humus. | Duration: 05/2023 - 04/2029
more info