| Duration: | 01/2024 - 12/2026 |
| Contracting Authority/ Sponsors: |
Federal Ministry for Digital and Transport (BMDV) |
| Project Partners: | ISRA Vision GmbH MeSys GmbH Carl Zeiss AG Hochschule Kempten |
| Project Focus: |
QUALLE – Quality Assurance in the Industrial Production of Fuel Cell CCMs

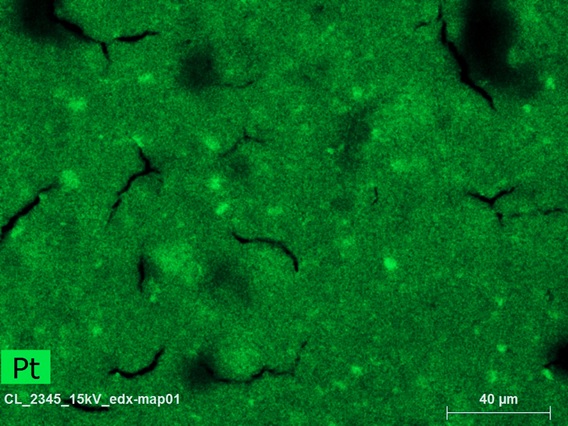
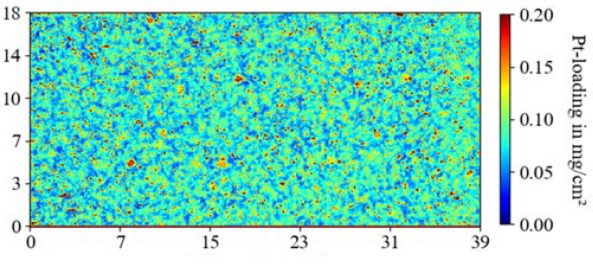
The "QUALLE" project brings together partners from industry and research with diverse expertise in quality assurance (QA) for PEM fuel cells. This HyFab project supports the further development of the industrial-scale production of catalyst-coated membranes (CCM), the heart of the PEM fuel cell, by enabling systematic testing with special analytical methods. Offline QA takes place after production, inline QA occurs on the assembly line and at-line QA uses production-compatible measuring times and conditions. The project develops and validates methods for each of the quality assurance measures. Extensive series of tests of different defects in different manifestations provide a valid assessment of the problem areas and thus significantly reduce rejects.
The core element of the PEM fuel cell is the catalyst-coated membrane (CCM), a polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) equipped with a catalyst layer on both sides. In order to achieve the planned market ramp-up for fuel cells, automated processes based on roll-to-roll (R2R) systems are required. However, during the production of CCMs, various types of defects can occur, the reliable detection of which is crucial for a high production yield of failure-free devices – in line with the quality requirements of the automotive industry.
In the production process for CCMs, the focus is on the individual layers (in particular the membrane and catalyst layer) at various stages of the process. Individual defects in a CCM can cause the complete failure of an entire fuel cell stack, which can consist of up to 400 CCMs. There are currently no sufficiently validated measurement methods for automated production to examine the manufacturing process of CCMs and their preliminary stages non-destructively for multiple defects at the high processing speeds required. In addition, the effects of the various kinds of defects remain largely unknown. In many cases, it is therefore still impossible to reliably predict the probability of failure of a CCM component and thus the failure of an entire fuel cell stack on the basis of the fault pattern.
The project aims to develop specifications based on the behavior of individual CCM components in single-cell operation. The knowledge obtained will thus provide a fault classification to serve as a go/no-go criterion for the planned further development of methods. The development of suitable analysis and QA methods is the objective of the QUALLE project.
The QUALLE project is being funded by the Federal Ministry for Digital and Transport Affairs (BMDV) with a total of 4,513,694.31 euros as part of the "National Innovation Program Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Technology" guideline. Funding for this measure is also provided as part of the German Recovery and Resilience Plan (DARP) via the European Recovery and Resilience Facilities (ARF) in the NextGenerationEU program. The funding guideline is coordinated by NOW GmbH and implemented by Project Management Jülich (PtJ).
