Urban photovoltaics (UPV) uses sealed surfaces in cities and municipalities to generate renewable electricity close to where it is needed, protecting people, the environment and buildings from the effects of the weather. Examples include large parking lots, public squares or sports facilities where photovoltaics are installed to provide shade, in combination with lighting, with charging infrastructure for electromobility or as rain protection. These installations improve the quality of stay and make the energy transition tangible. One example is the integration of photovoltaics, lighting, shade and rain protection at a central bus station or in the parking lot of an exhibition center. PV systems can also serve as advertising billboards on roads and integrate WiFi or 5G mobile communications.
UPV installations must meet high standards of functionality and design and often require individual solutions. In addition, the legal framework conditions in publicly accessible areas and the approval procedures are complex.
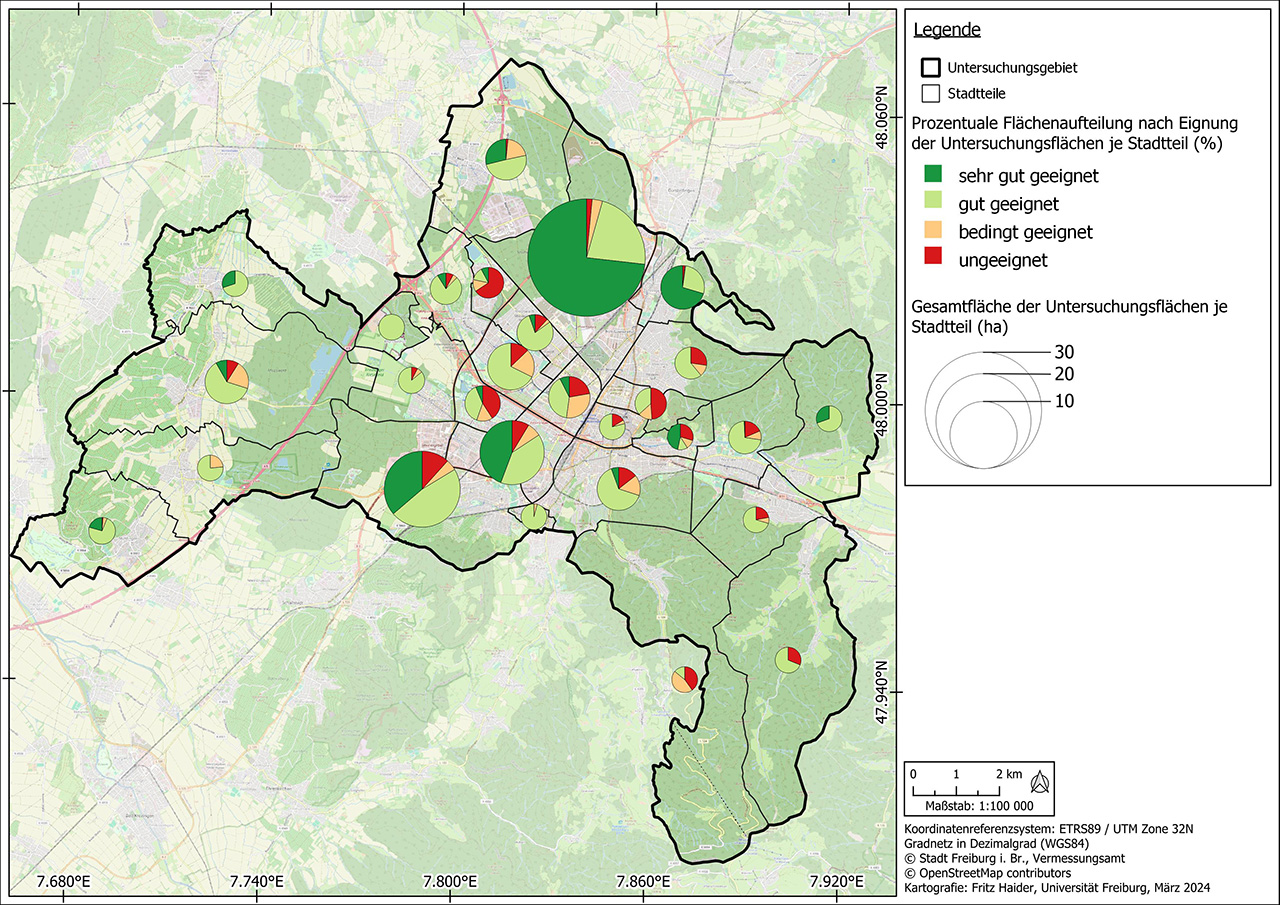
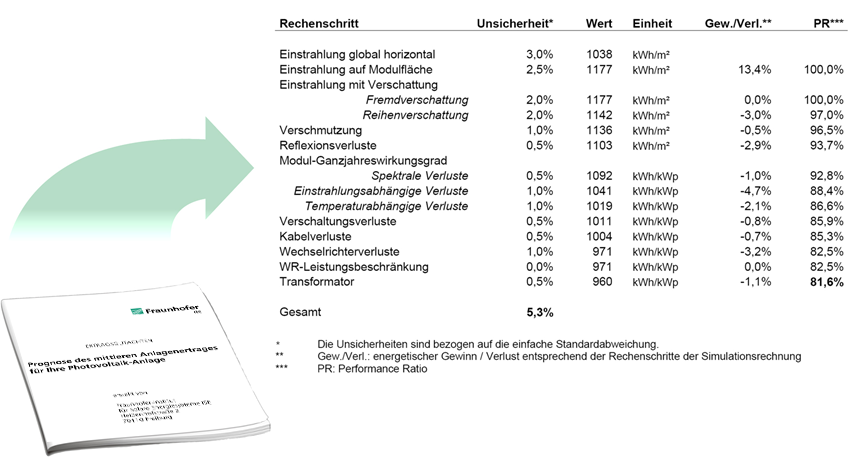
Our research work on urban photovoltaics includes analyzing the potential of areas, output and yield of PV systems. We prepare yield assessments and develop design plans that ensure the economic optimization of PV systems, stationary batteries, fast-charging stations and grid connections. We also carry out life cycle analyses and calculate the CO2 footprint, for example by comparing steel and wooden substructures.
With our scientific work, we support the development of optimal and sustainable solutions for urban photovoltaics and contribute to the successful implementation of the energy transition in urban areas.