| Duration: | 03/2021 - 02/2024 |
| Contracting Authority/ Sponsors: |
Bundesministerium für Wirtschaft und Energie (BMWi) |
| Project Partners: | Öko-Institut; Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg, Institut für Nachhaltige Technische Systeme (INATECH); Hochschule Offenburg |
| Project Focus: |
IND-E – Decarbonization and Electrification Potentials of the German Industry
Data, stakeholders and models
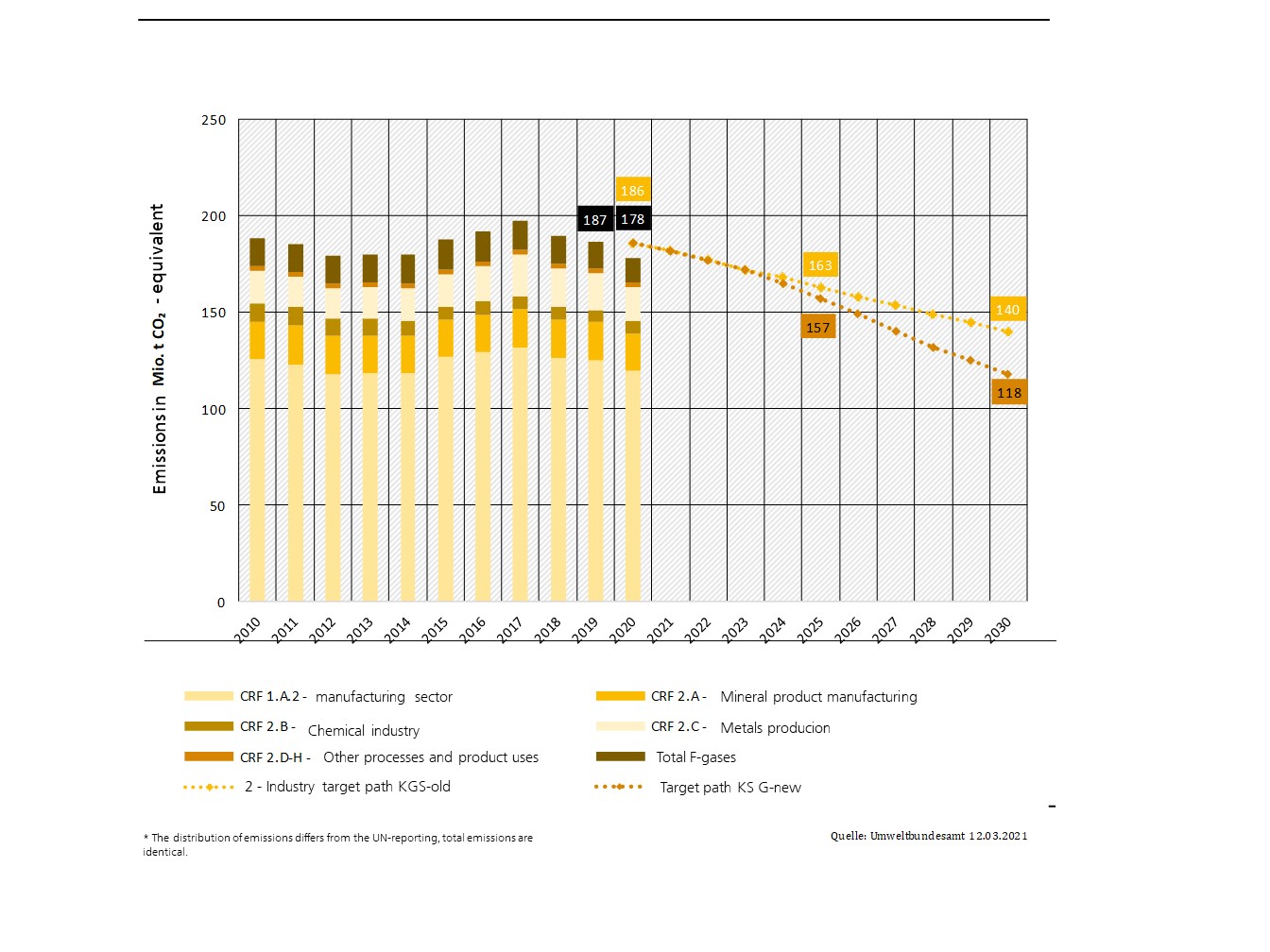
According to the Federal Environment Agency, industry emitted around 178 million metric tons of greenhouse gases in Germany in 2020, accounting for 22% of Germany's greenhouse gas emissions. The German government has set itself the target of climate neutrality by 2045, which poses major challenges for the industrial sector. Within the scope of the research project "IND-E", decarbonization potentials and barriers will be identified and further analyzed. In addition, various energy system models - from energy system models and electricity market models to models that represent single industrial companies or areas - are being further developed and combined. Thus, the complex interrelationships of industrial decarbonization and the urgent questions regarding the decarbonization of industry can be addressed using a broad model landscape.
The project is being carried out in close cooperation with the project partners Oeko- Institut, University of Freiburg (INATECH), University of Applied Sciences Offenburg and Fraunhofer ISE (project coordination). The project is divided into three main parts.
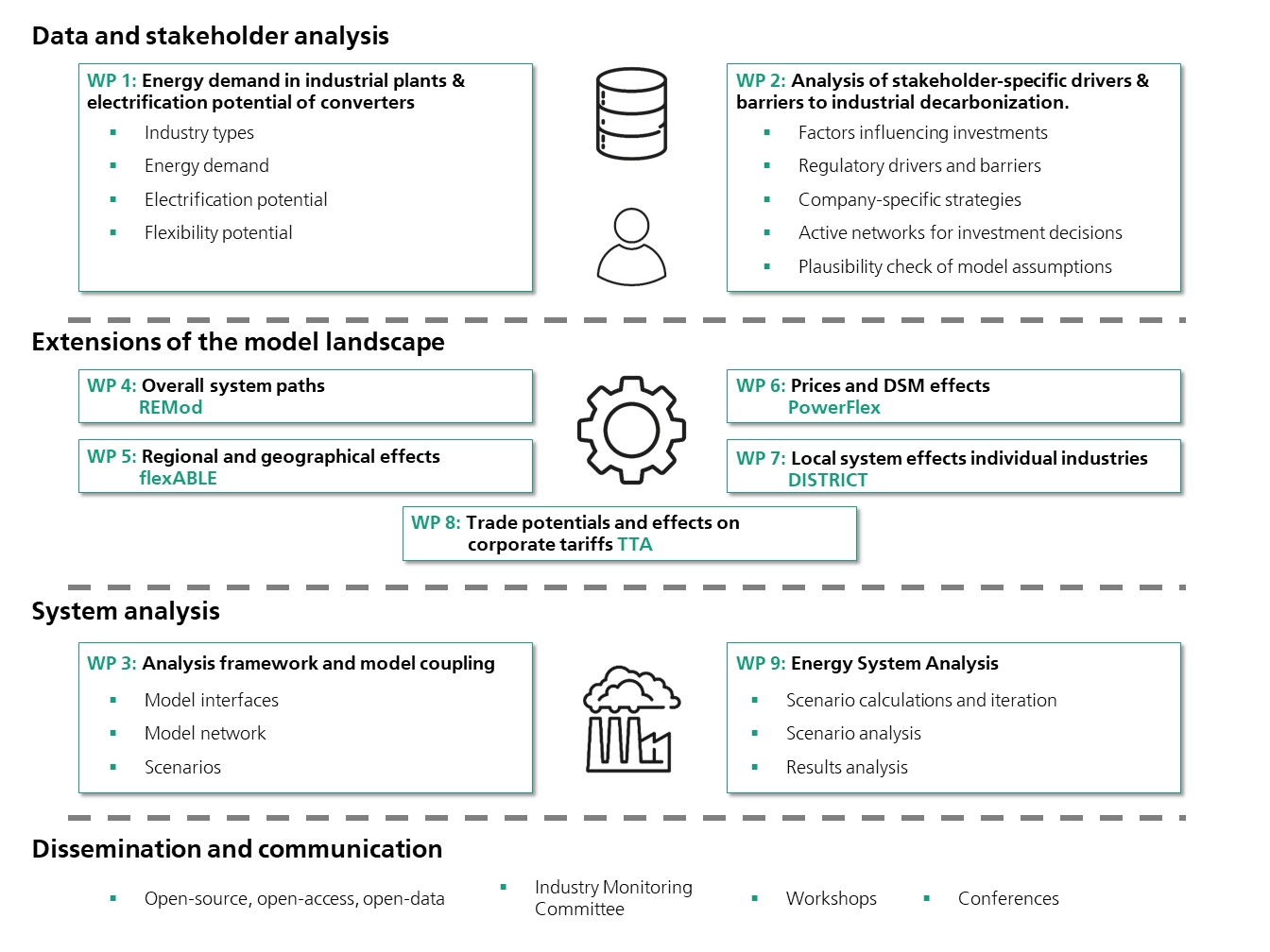
The data and stakeholder analysis aims to capture and generate industrial demand load profiles and electrification and flexibility potential by industry type so that they can be used in energy system models. The synthetic load profile time series will be published so that they are freely available to the scientific community. Furthermore, investment decisions of industrial companies in climate-friendly technologies will be investigated. For this purpose, the influencing factors of investments, regulatory drivers and barriers as well as company-specific strategies will be investigated and correlated in impact networks. In addition, the stakeholder analysis serves to plausibilize the assumptions on technology diffusion of the system models. The work is carried out in close cooperation between Fraunhofer ISE and Oeko- Institut.
The second focus of the project is the expansion of the model landscape. Within the consortium, five existing models or models to be developed are represented: Fraunhofer ISE's intersectoral energy system model REMod to map transformation pathways, INATECH's flexABLE model on regional effects, in particular the impact on the power system and grid , Oeko- Institut 's Power-Flex model to map power plant deployment at the European level, and the DISTRICT model to map individual industries or industrial areas. The TTA model is being developed by the Offenburg University of Applied Sciences to map trading potentials and effects on corporate tariffs.
In the area of system analysis, a framework is created that enables data exchange between the models and model iterations to be carried out. This model framework is applied to calculate different scenario worlds of industrial decarbonization and to analyze their effects.
The project is being carried out with the close involvement of the Industry Advisory Board consisting of the Association of German Chambers of Industry and Commerce e. V., the Federation of German Industries e.V. and the Freiburg Chamber of Commerce and Industry.