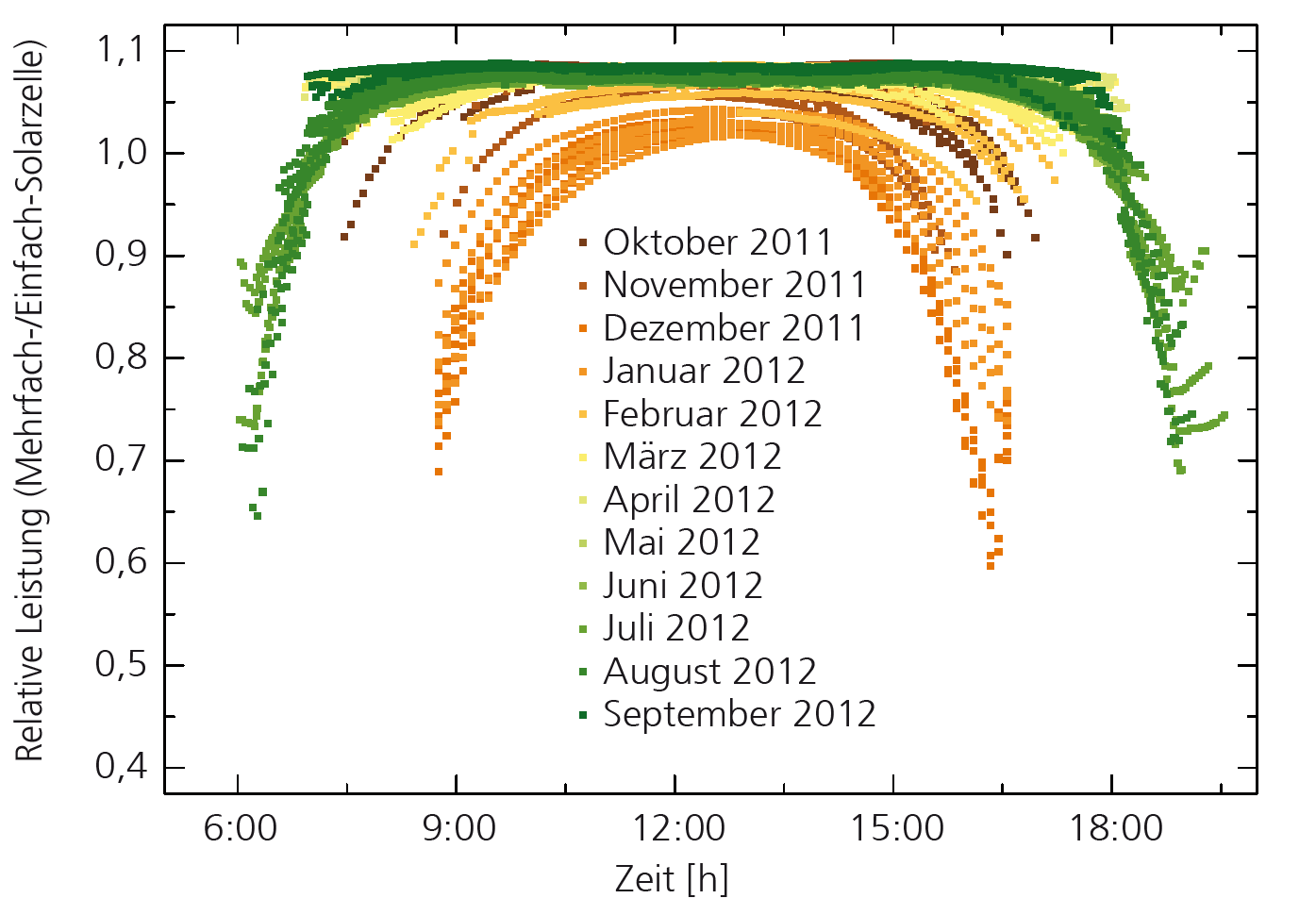
An impressive record efficiency value of 33.3 % for a silicon-based multi-junction solar cell was achieved at Fraunhofer ISE with a III-V-on-silicon tandem solar cell. But how does this type of cell perform at the module level? And what is the energy yield of modules with multi-junction solar cells in comparison to single-junction solar cells, if a complete year and the solar radiation at a specific location is taken into account? These questions are also very important for the emerging perovskite-on-silicon tandem solar cells.
From the Tandem Record Cell to Yield Analysis
Emerging Photovoltaic Technologies
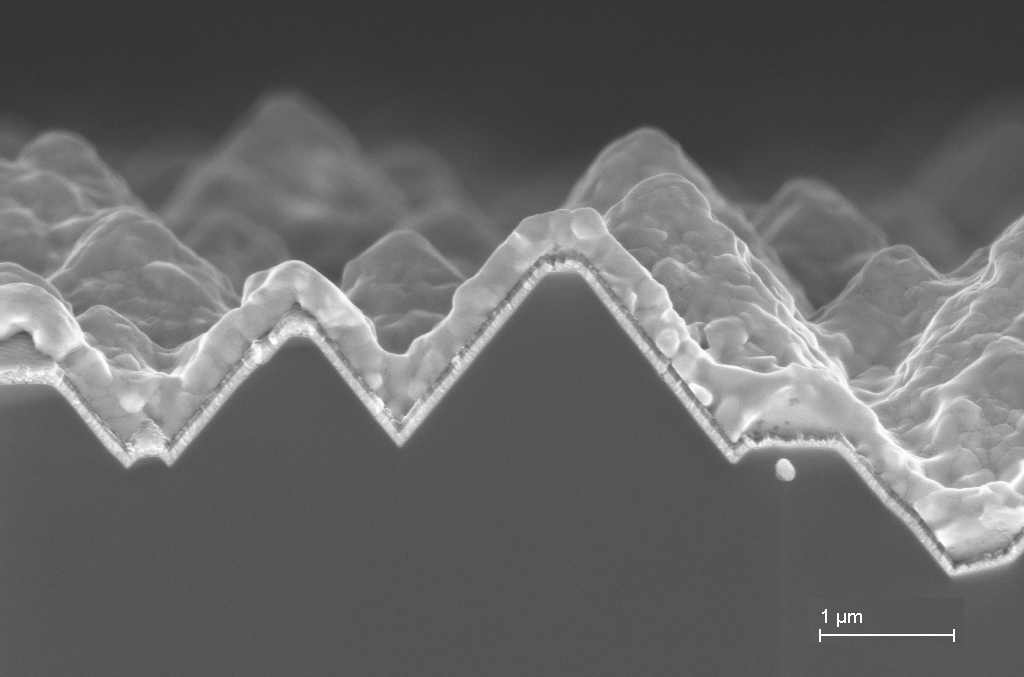
In a simulation-based approach to answer these questions, the »OPTOS« and »YieldOpt« tools that had been developed at Fraunhofer ISE were connected with each other. »OPTOS« allows tandem solar cells with an arbitrary number of layers and different surface structures to be optically modelled efficiently at the cell and module level. Important decisions concerning the selection of materials or structure parameters can already be made and optimized on this basis. The spectrally resolved absorptance that is calculated with »OPTOS« is also an important component for further analysis with »YieldOpt«. This tool connects the optical and electrical simulation of the solar cell with the incident solar spectrum that is determined by measurement or simulation. In this way, different solar cell concepts can be modelled under realistic conditions and their yield in the field can be estimated and compared.