| Duration: | 07/2021 - 06/2024 |
| Contracting Authority/ Sponsors: | Projektträger Karlsruhe, Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF) |
| Project Partners: | Technische Universität Berlin (TUB), Prof. Dr.-Ing. Sven-Uwe Geissen; inter 3 GmbH - Institut für Ressourcenmanagement (inter3), Dr.-Ing. Shahrooz Mohajeri; Qatar University (QU), Prof. Dr. Sami Sayadi; University of Birjand (UBi), Dr. Mohsen Pourreza Bilondi; Isfahan University of Technology (IUT), Banafshe Khalili, PhD |
| Website: | HighRec; www.highrec.de |
| Project Focus: |
HighRec – Enhancement of the recovery ratio in brackish water desalination systems for agricultural irrigation
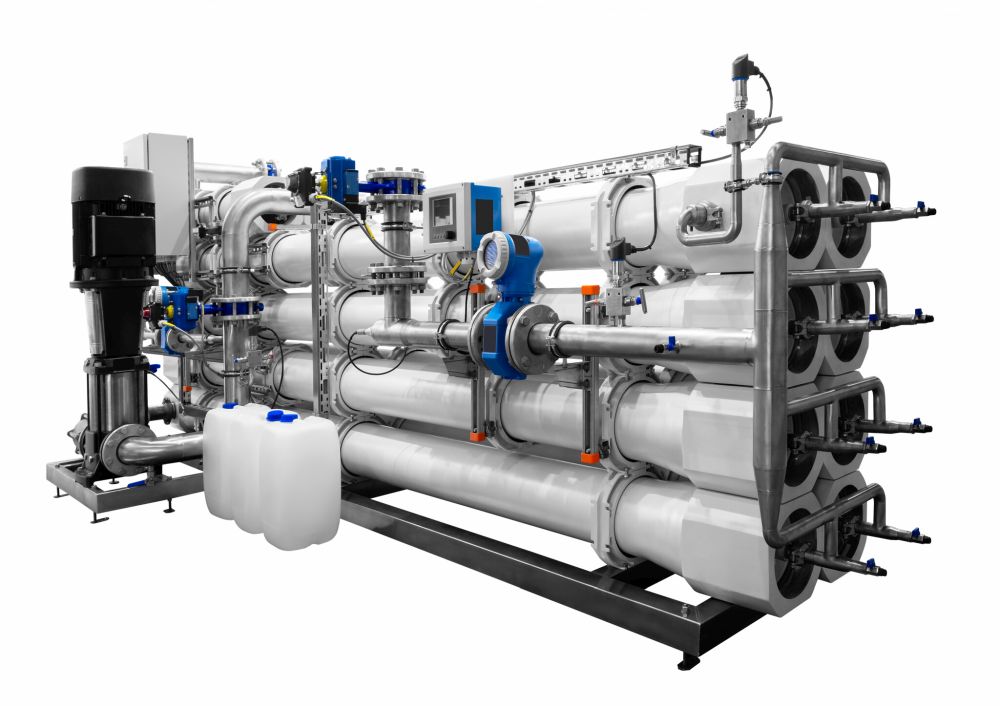


In many places in the Near East, water demand for agriculture exceeds available freshwater resources, creating new challenges for the sector. In view of water scarcity, technologies are needed to increase water availability to avoid negative impacts on crops. The use of desalination plants coupled with renewable energy can increase water availability for irrigation with minimal environmental impact. The HighRec project will promote the sustainable use of brackish water through desalination with solar energy. It will also investigate the ability of the treatment process to produce fresh water of suitable quality, the plant design that is appropriate for agricultural use, and the impact of the treatment plant on crop yields.
The aim of the project is to develop a flexibly operating brackish water desalination plant for different raw water compositions with fluctuating energy supply to obtain fresh water for agriculture.
The high energy demand, which varies depending on the salinity, is to be covered by solar energy, ensuring operation with the lowest possible environmental impact in terms of CO2 emissions. The process operation of reverse osmosis with a closed high-pressure circuit as a semi-batch operation enables a high recovery of water, innovative operation control strategies for flexible adaptation to fluctuating energy supply and raw water composition, as well as minimization of the chemicals to be used and the amount of brine to be disposed. Concepts against silica and sulfate scaling and for environmentally friendly brine disposal will be part of the plant design to ensure a sustainable and economic use and to recover as much usable water as possible. A demonstration plant will initially be installed at a hydroponic greenhouse facility in Qatar in the fall of 2023, allowing the developed concept to be tested and analyzed under real-world conditions. The demonstrator's next stop will then be a saffron farm near Birjand in Iran. The success of the project is to be achieved not only through the practical suitability of the plant, but also through the collection of technical and economic data for market introduction and a transdisciplinary exchange of knowledge. For this purpose, the involvement of the education sector is planned in order to create a long-term exchange platform in the academic field as well as with partners from the practical implementation.
