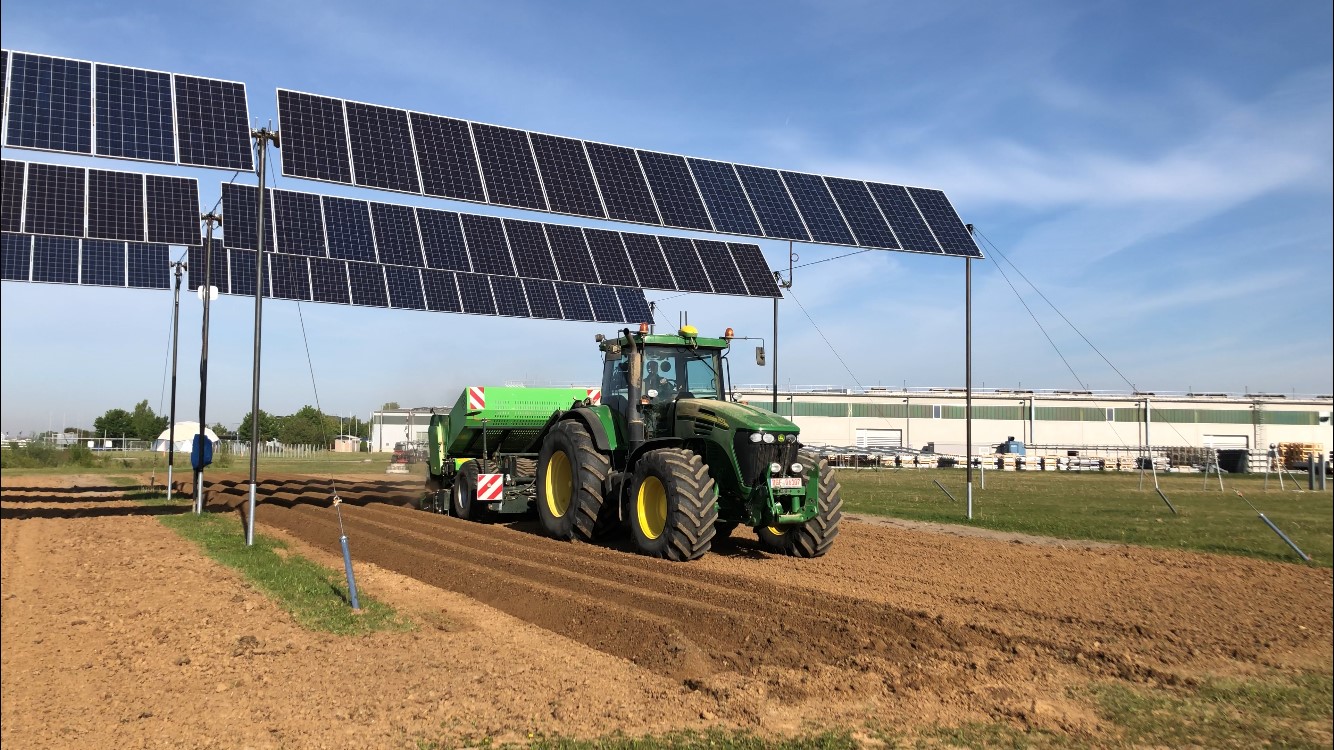
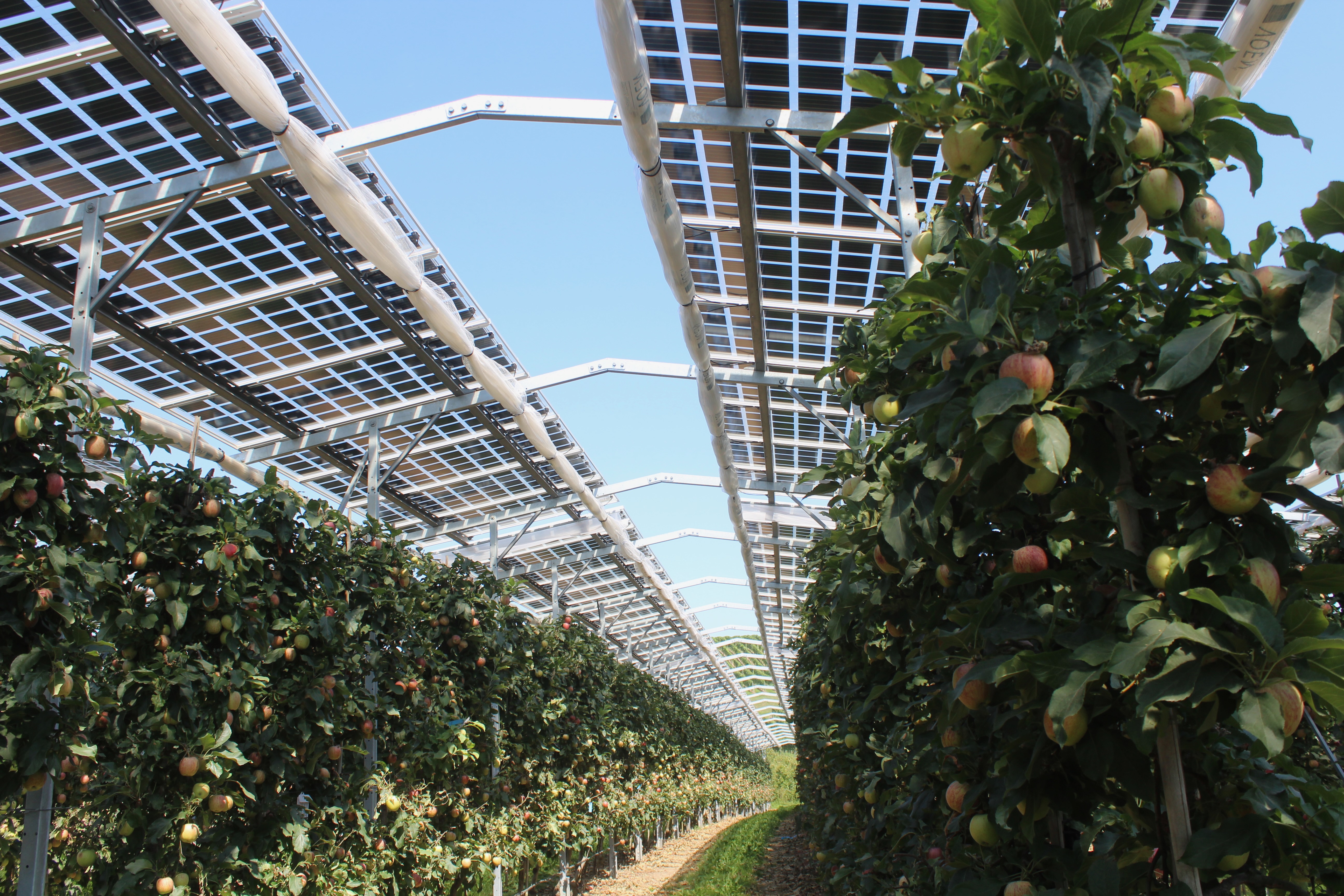
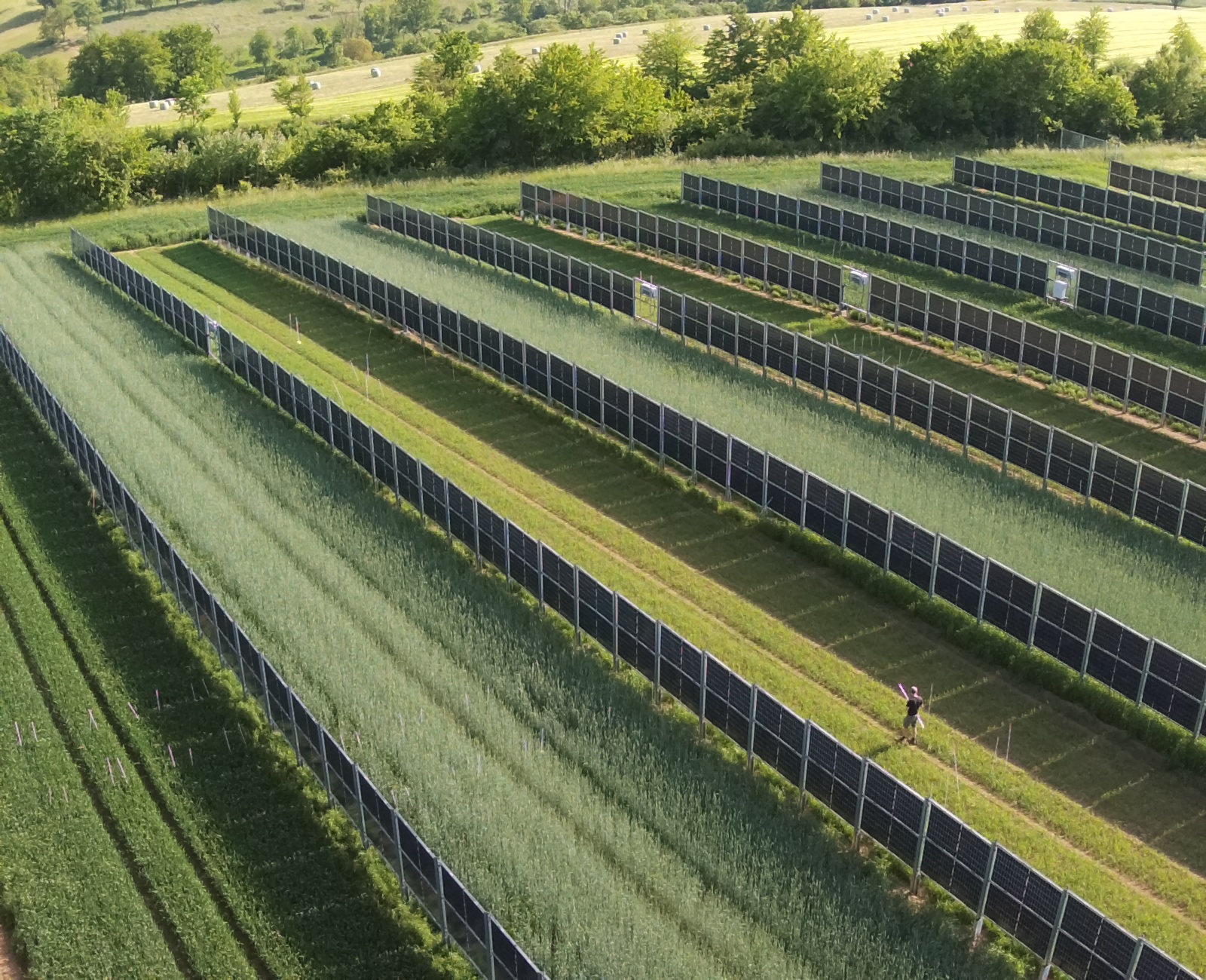
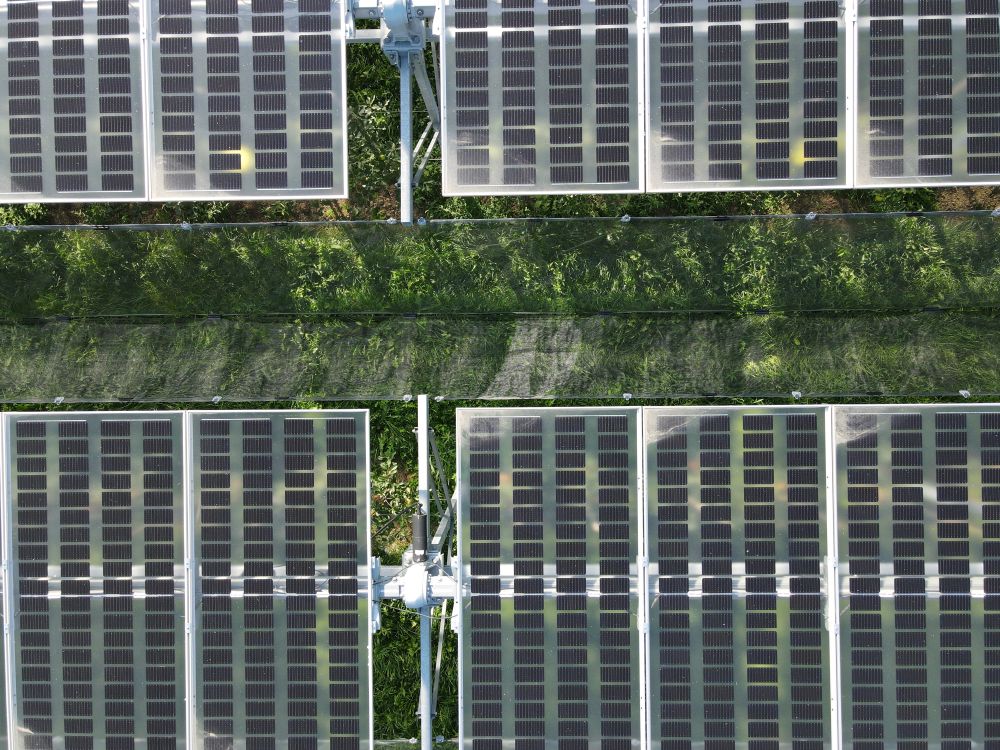
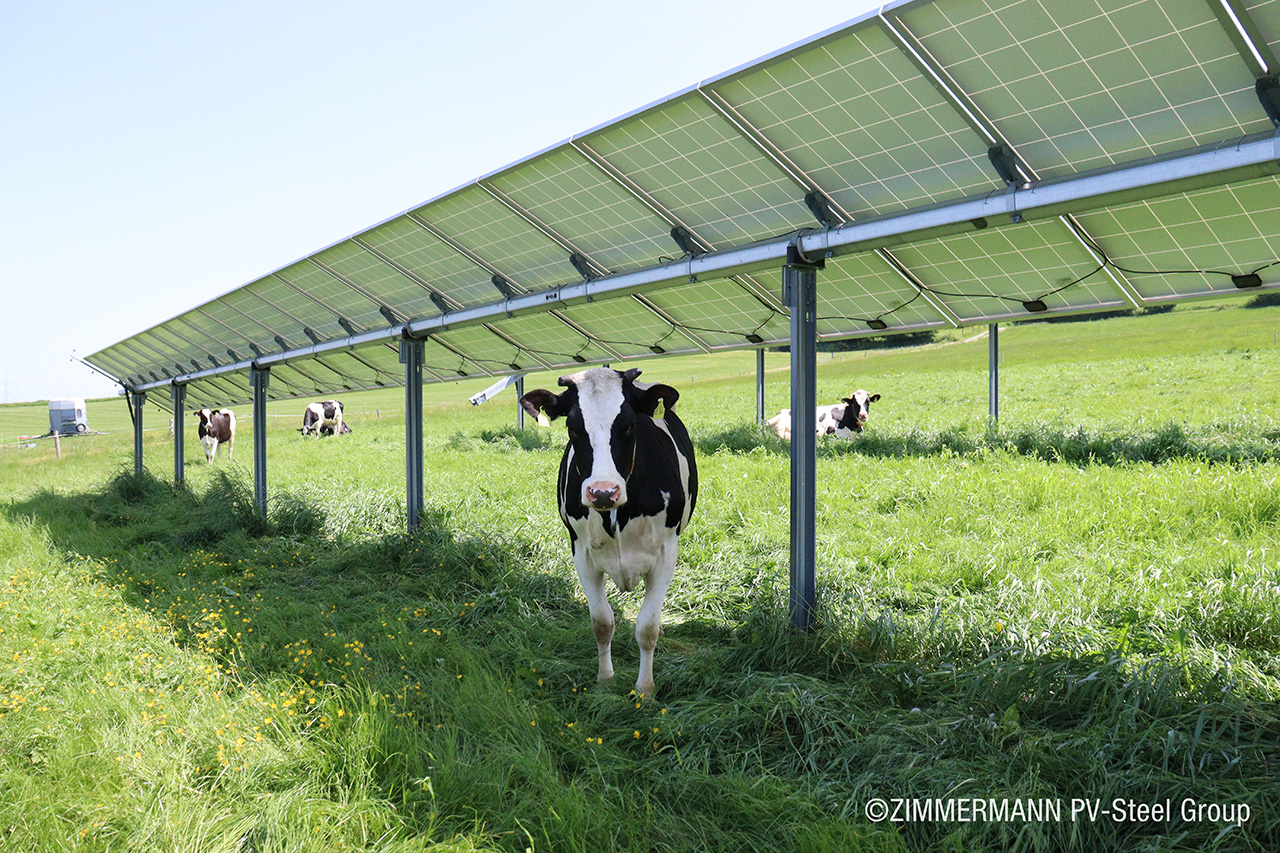
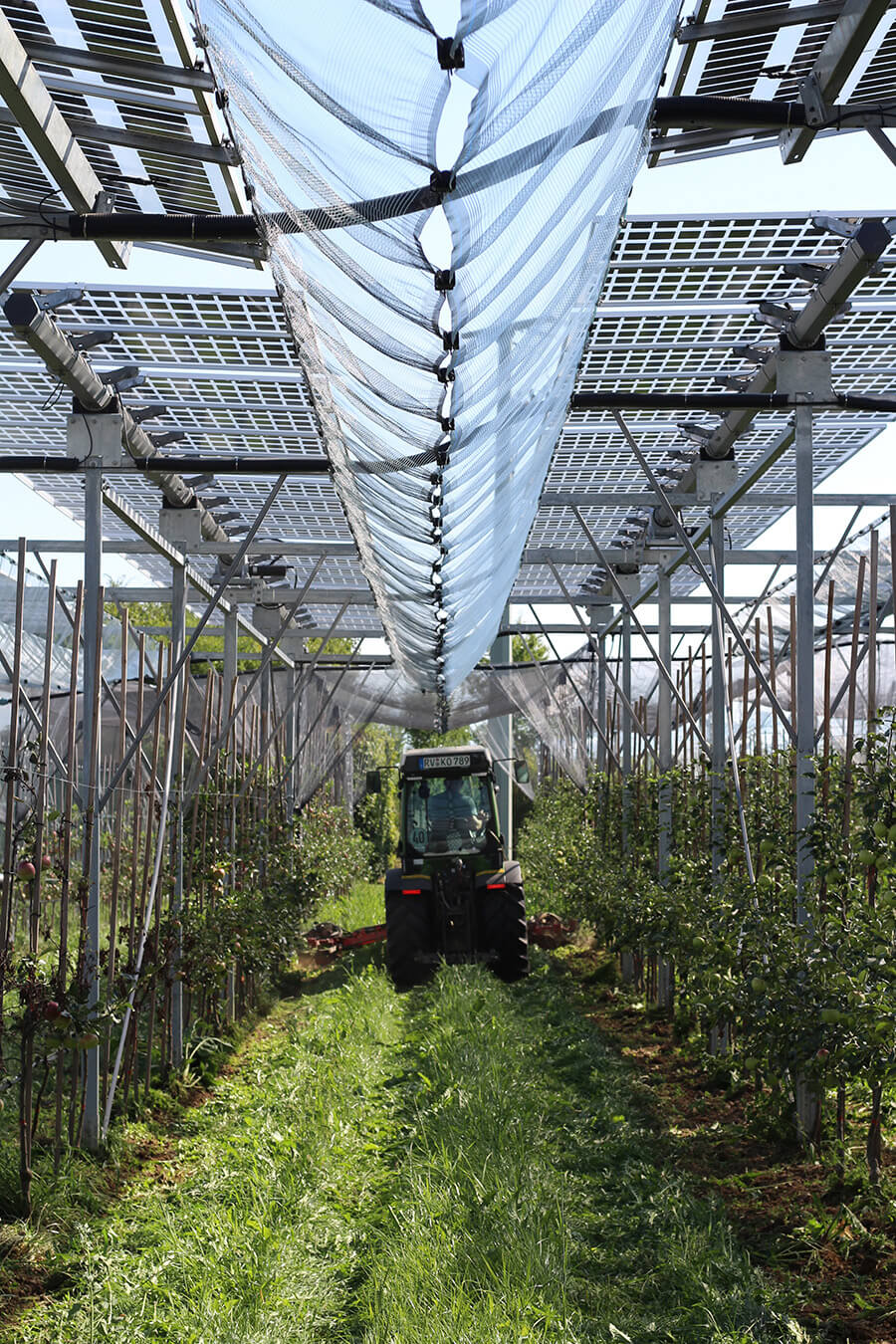
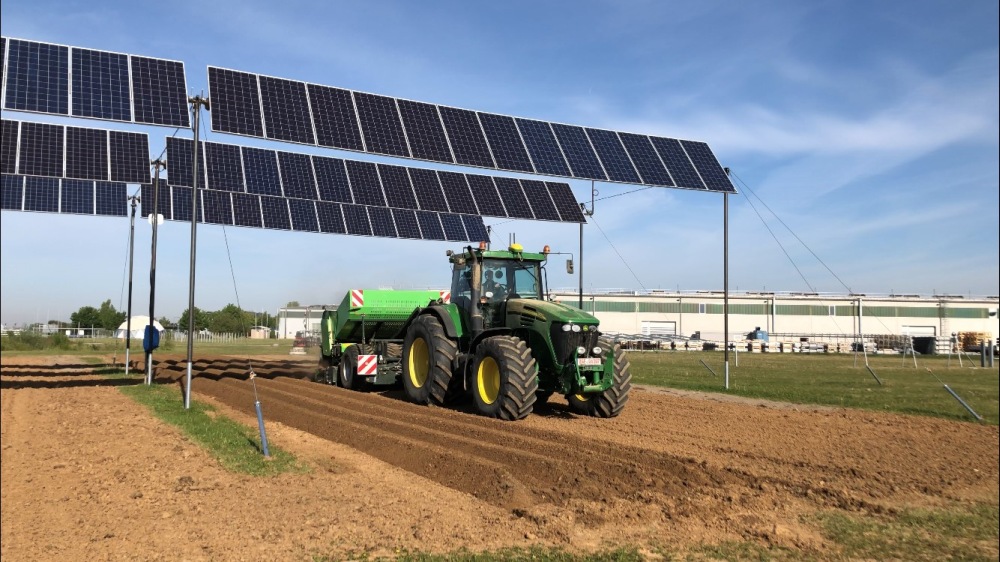
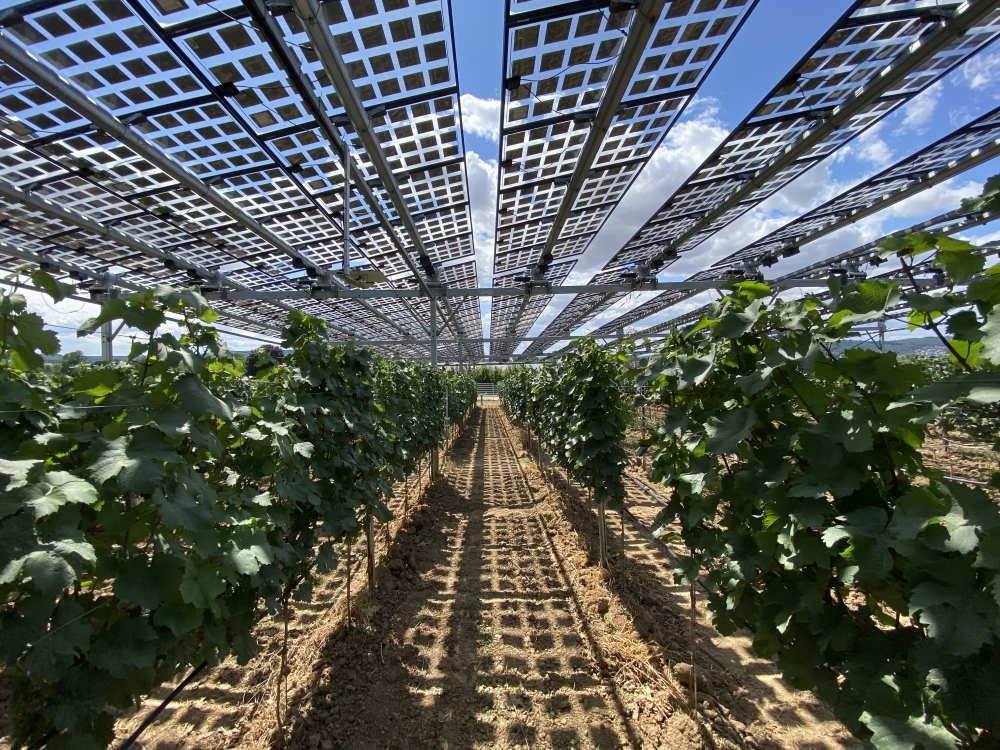
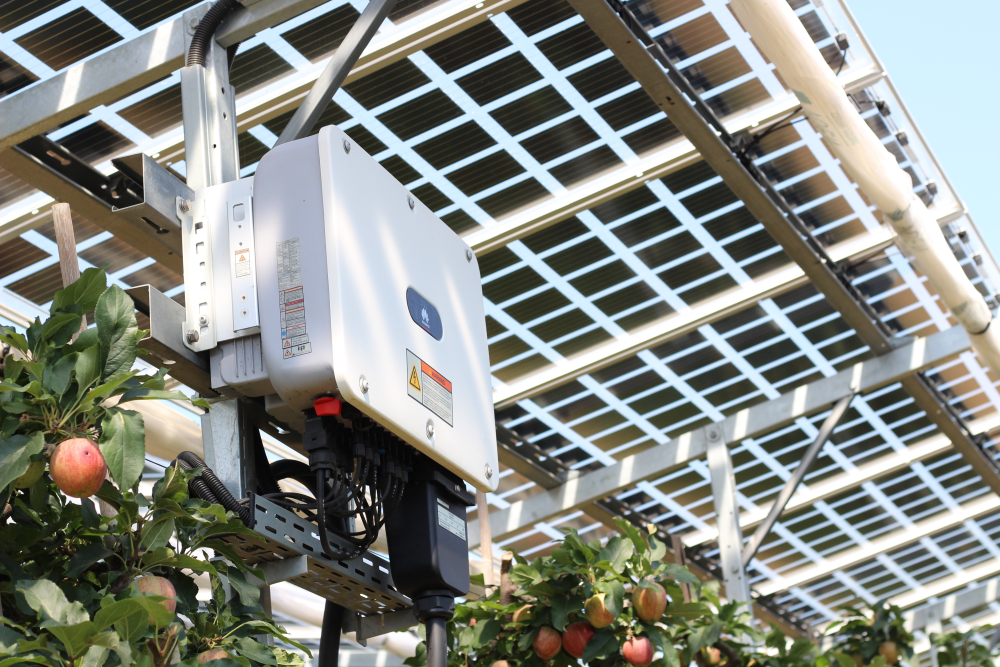
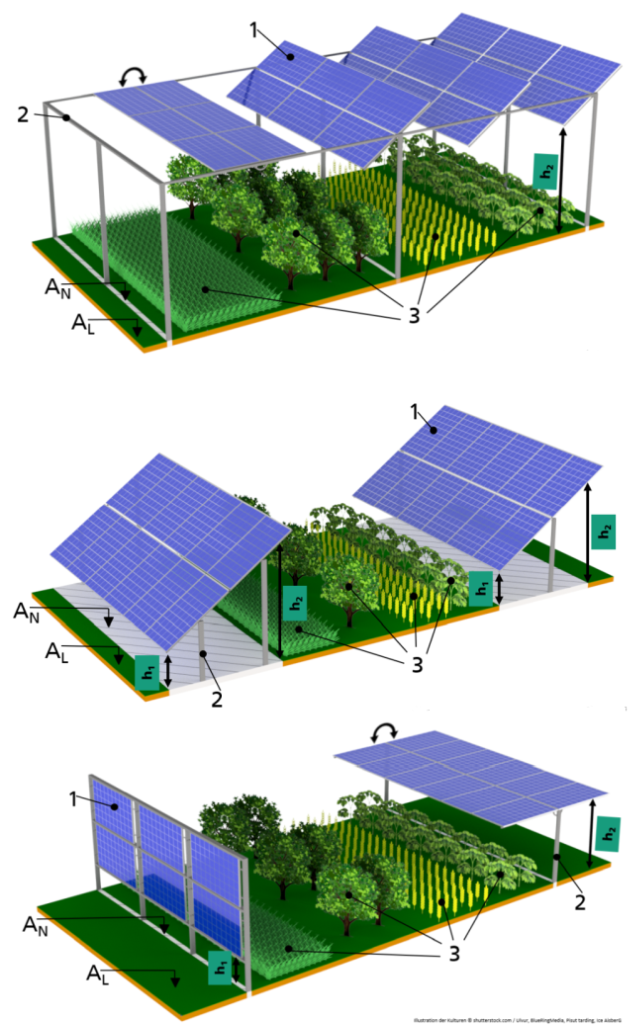
Agrivoltaics describes a process for the simultaneous use of agricultural land for food production and PV power generation. The technology enables the efficient dual use of agricultural land: photovoltaics on open spaces can be substantially expanded without significantly using up valuable resources of fertile arable land. Targeted light management optimizes the yields from PV and photosynthesis. In addition, value creation in the region and rural development are promoted, as agrivoltaic projects are ideally suited to be supported in a decentralized by farmers, municipalities and small and medium-sized enterprises. This results in new, economically viable farming options for agriculture.
We are working on the implementation and further development of agrivoltaics in industrial and research projects.